Why Agile maturity matters for transformation leaders
Agile, once confined to isolated teams, has gradually transformed into a cornerstone of strategic success at the enterprise level. For transformation leaders – CIOs, COOs, and PMO heads – the real challenge lies in scaling Agile across the organization in a way that integrates with overarching strategic objectives. While Agile adoption at the team level may seem straightforward, achieving enterprise-wide impact requires a fundamentally different approach.
Assessing your organization’s current level of Agile maturity is a critical first step in bridging this gap and achieving meaningful transformation.
💡 What is Agile Maturity? Agile maturity measures an organization’s capability to adopt, scale, and sustain Agile practices across teams, portfolios, and business functions. It reflects not just the implementation of Agile frameworks but also how deeply Agile principles are embedded in the organization’s culture, decision-making processes, and ability to deliver strategic outcomes.
Achieving Agile maturity means embedding Agile principles into the core of your organization’s operations, decision-making, and strategic planning.
This guide outlines key dimensions of Agile maturity – strategic alignment, transparency, collaboration, and scalability. By assessing these areas, you can pinpoint current capabilities and identify focused actions to strengthen your organization’s maturity, ensuring Agile becomes a strategic driver for transformation.
What are the stages of Agile maturity?
The stages of Agile maturity define how effectively Agile principles are integrated across an organization’s teams, portfolios, and strategic objectives.
This section provides a framework for evaluating Agile maturity, helping you determine where your organization stands today and what’s required to embed Agile as a systemic, enterprise-wide practice.
image:medium
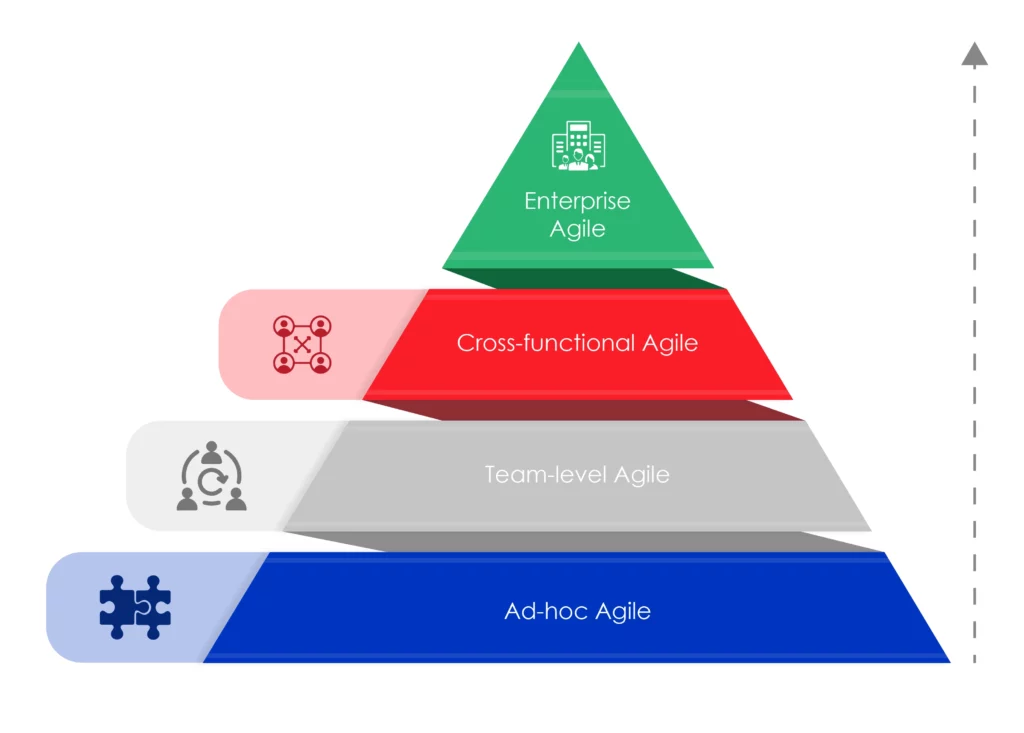
1. Ad-hoc Agile
At the Ad-hoc stage, Agile practices emerge sporadically, often driven by individual teams exploring methods like Scrum or Kanban. However, these efforts lack formalized structure, leadership support, or alignment with broader business goals. As a result, Agile remains fragmented and fails to deliver value beyond isolated teams.
Key characteristics:
- Agile methods are used inconsistently across the organization, with teams working in silos.
- Visibility into Agile efforts is limited, making it difficult to connect team-level activities with strategic objectives.
- Reporting and resource forecasting rely on basic, manual processes.
Challenges:
- Inconsistent practices lead to uneven outcomes and missed opportunities for collaboration.
- Scaling Agile across portfolios is difficult without standardized frameworks and governance.
- The lack of strategic visibility and alignment limits the ability to measure or optimize Agile’s impact.
💡 At this stage, organizations often focus on foundational elements, such as creating a common understanding of initiatives, implementing basic budget tracking, and beginning to standardize reporting. Moving beyond this phase requires leadership to drive alignment and visibility, laying the groundwork for formal Agile maturity.
2. Team-level Agile
At the Team-Level stage, Agile practices are more established and consistent within individual teams, resulting in improved delivery speed and operational efficiency. However, these gains remain confined to team silos, with limited visibility or connection to broader organizational goals. For large enterprises, this stage highlights the need to move beyond isolated successes toward a more integrated approach.
Key characteristics:
- Teams have adopted Agile frameworks such as Scrum or Kanban with measurable improvements in productivity and delivery.
- Teams operate independently, with little coordination or shared processes across departments.
- Delivery reporting is limited to team-level metrics, providing minimal visibility at the portfolio level.
Challenges:
- Siloed teams hinder collaboration, making it difficult to scale Agile practices across the organization.
- Misalignment between team-level outcomes and strategic priorities prevents Agile from driving enterprise-wide value.
- Leadership perception of Agile as a purely operational tool limits its adoption as a strategic enabler.
💡 At this stage, organizations begin to focus on financial control, introducing cost tracking, risk management, and basic reporting across teams.
3. Cross-functional Agile
At the Cross-functional Agile stage, organizations begin bridging the gap between isolated teams and broader business objectives. Teams collaborate across functions, and Agile practices gain visibility and traction at higher levels. Leaders start to recognize Agile as a strategic asset, but challenges remain in scaling these practices consistently across the enterprise.
Many organizations linger in this phase, as it requires navigating complex coordination, aligning teams with strategic themes, and establishing governance structures that balance flexibility with oversight. Although progress can feel gradual, this stage is pivotal for building the foundations necessary to achieve enterprise-wide agility.
Key characteristics:
- Teams collaborate across functions, moving beyond silos to align delivery with broader strategic goals.
- Basic governance structures and visibility mechanisms are introduced to track progress, performance, and resource allocation.
- Delivery reporting evolves to provide insights across multiple departments, improving transparency and accountability.
Challenges:
- Scaling Agile consistently across diverse functions remains complex, particularly in large organizations.
- Aligning Agile initiatives with long-term business strategy requires more robust governance and cross-department coordination.
- Leaders may struggle to strike the right balance between maintaining oversight and allowing the flexibility Agile demands.
💡 At this stage, organizations begin to move toward an SPM (Strategic Portfolio Management) approach. Initiatives align more closely with strategic themes, team-centric cost tracking emerges, and basic lifecycle governance takes shape. This progress builds the necessary foundation for scaling Agile as a systemic, enterprise-wide practice.
4. Enterprise Agile
Enterprise Agile represents a fully mature state where Agile principles are embedded across the organization, aligning strategy, execution, and delivery. At this stage, Agile transitions from a set of team-level practices into a scalable, systemic framework that drives business value across portfolios and functions. Enterprise Agile enables organizations to adapt to market changes, scale innovation, and ensure every initiative contributes to long-term strategic goals.
Key characteristics:
- Agile is deeply embedded in the organization’s culture and operating model, acting as a strategic enabler at every level.
- Teams operate with autonomy while maintaining alignment with the organization’s priorities and strategic themes.
- Real-time governance frameworks provide visibility into portfolio performance, resource allocation, and value realization.
Challenges:
- Balancing the autonomy of teams with governance frameworks to ensure consistency and alignment at scale.
- Managing the complexity of large, interconnected portfolios while maintaining agility and fostering innovation.
💡 At this stage, organizations gain the visibility, alignment, and governance required to manage complex portfolios and deliver measurable outcomes at scale. Enterprise Agile ensures initiatives remain strategically aligned while equipping teams to adapt and deliver value in dynamic environments.
Key dimensions of Agile maturity
To assess Agile maturity effectively, organizations must evaluate how well Agile principles are integrated into core areas of culture, strategy, and operations.
This section introduces four key dimensions of Agile maturity:
- Strategic alignment
- Visibility and governance
- Culture and collaboration
- Scalability
Each dimension includes reflection points to help you determine your organization’s current state, uncover areas for improvement, and identify specific steps to advance Agile practices.
1. Strategic alignment
At the core of any successful Agile transformation is the ability to align Agile initiatives with organizational strategy. In large enterprises, misalignment between Agile teams and business goals often reduces Agile to a series of operational improvements rather than a driver of enterprise-wide success.
Questions to reflect on:
- How effectively are Agile initiatives connected to your organization’s strategic objectives?
- Do teams understand how their work contributes to delivering business priorities?
- Is there a feedback mechanism (e.g., retrospectives or performance reviews) that evaluates Agile outcomes against strategic performance?
Indicators of maturity:
High: Agile is embedded as a strategic enabler. Teams work with a clear understanding of leadership priorities, and performance is evaluated based on progress toward strategic goals.
Low: Agile operates in isolation, with team-level outputs disconnected from overarching business objectives. Leadership lacks visibility into Agile’s contribution to strategy.
Next steps:
- Engage leadership in defining and communicating how Agile initiatives support enterprise priorities.
- Implement portfolio management practices that create a clear link between Agile efforts and strategic goals. Focus on aligning initiatives, measuring value delivery, and improving visibility across teams and portfolios.
2. Visibility & Governance
Lack of visibility into Agile initiatives is one of the most persistent challenges for large enterprises. Effective governance frameworks provide clarity while preserving the flexibility Agile relies on to deliver results.
Questions to reflect on:
- Do you have comprehensive visibility into Agile initiatives at the team, departmental, and portfolio levels?
- Is your governance approach enabling leadership oversight without creating unnecessary bottlenecks?
- Can you reliably measure Agile performance, track portfolio health, and connect outcomes to strategic goals?
Indicators of maturity:
High: Governance structures are well-defined, providing leadership with the data needed to oversee performance and ensure alignment without micromanaging teams. Portfolio visibility enables data-driven decision-making and supports timely adjustments.
Low: Visibility is fragmented, with limited tracking of team performance or portfolio progress. Governance structures are absent or overly rigid, stifling Agile flexibility and slowing decision-making.
Next steps:
- Introduce governance practices that ensure portfolio-level visibility without undermining Agile principles. Focus on creating a framework that balances autonomy with accountability.
- Leverage tools that consolidate progress metrics, portfolio health, and performance insights into a centralized view, enabling leadership to make informed decisions and identify areas requiring intervention.
3. Culture & Collaboration
A key marker of Agile maturity is an organization’s ability to foster a culture that embraces Agile principles and enables meaningful collaboration across teams. In large enterprises, success hinges on breaking down silos, encouraging cross-functional alignment, and embedding Agile values at every level, from leadership to team members. Without these cultural shifts, Agile efforts risk fragmentation and stagnation.
Questions to reflect on:
- Does your organization actively promote collaboration across teams, departments, and portfolios?
- Are Agile principles consistently modeled by leadership and integrated into decision-making processes?
- Is there a culture of continuous improvement that empowers teams to experiment, adapt, and evolve their practices?
Indicators of maturity:
High: Teams collaborate fluidly across functions, guided by shared Agile values. Leadership champions Agile principles, fostering trust, adaptability, and a culture of learning.
Low: Teams remain isolated within functional silos, with Agile adoption fragmented and limited to individual groups. Leadership does not actively support Agile values, creating barriers to collaboration and enterprise-wide integration.
Next steps:
- Promote cross-team collaboration by creating structures for knowledge sharing, joint planning, and shared accountability for outcomes.
- Equip leadership with the tools and training to model Agile principles, ensuring alignment across the organization and reinforcing a culture of trust and adaptability.
4. Scalability
For large enterprises, scaling Agile beyond individual teams is one of the most complex challenges. Achieving scalability means addressing the complexities of enterprise-wide operations without losing the adaptability and flexibility that Agile offers.
Questions to reflect on:
- How effectively have Agile practices been scaled from individual teams to the broader enterprise?
- Are there consistent frameworks and tools that allow teams to tailor Agile practices while ensuring alignment with enterprise goals?
- What obstacles have emerged when scaling Agile across functions, portfolios, or global regions?
Indicators of maturity:
High: Agile practices are fully scalable, supported by frameworks, leadership alignment, and tools that enable adaptability while maintaining strategic focus. Teams operate independently yet stay connected to enterprise priorities.
Low: Scaling efforts are inconsistent, with varying frameworks and practices across teams. Leadership struggles to provide the support or governance needed to achieve scalability. Misalignment between team execution and enterprise goals hampers progress.
Next steps:
- Develop and implement standardized Agile frameworks that balance consistency with adaptability, enabling teams to scale while staying aligned with enterprise objectives.
- Invest in tools and practices that simplify the management of large portfolios, offering transparency, real-time insights, and the flexibility to adapt as priorities shift.
Assessing your Agile maturity
This scoring framework will help you gauge your level of maturity and identify specific areas for improvement.
By the end of this section, you’ll have an understanding of whether your organization is operating at an Ad-hoc, Team-Level, Cross-Functional, or Enterprise Agile maturity level.
How to score your organization
Rate your organization on a scale of 1 to 5 for each of the four dimensions, based on the characteristics and questions outlined earlier:
1 = Very Low Maturity
- Minimal or no integration of Agile practices.
- No alignment with broader strategic goals.
2 = Low Maturity
- Agile practices exist but are inconsistent or limited to specific teams.
- Little measurable impact on broader organizational performance.
3 = Moderate Maturity
- Agile practices are consistent within teams and starting to align with organizational objectives.
- Significant gaps remain in integration and scalability.
4 = High Maturity
- Agile practices are well-integrated and aligned with strategic goals.
- Clear improvements are visible across teams and portfolios.
5 = Very High Maturity
- Agile is fully embedded across the organization, enabling strategic alignment and systemic value delivery.
- Practices are scalable, adaptive, and consistently driving enterprise-wide outcomes.
Use your scores to identify strengths and weaknesses in each dimension. For areas with lower scores, revisit the reflection questions and next steps provided earlier to develop a targeted action plan.
Dimension 1: Strategic alignment
Evaluate how well Agile initiatives align with your organization’s strategic business goals.
- 1-2: Agile operates as a tactical tool, disconnected from business objectives, with no clear link to strategic outcomes.
- 3-4: Agile efforts are increasingly aligned with strategy, but silos persist, and not all teams understand how their work supports broader goals.
- 5: Agile is a core part of the strategic vision, with every initiative directly contributing to long-term business priorities.
Dimension 2: Visibility & governance
Assess your organization’s ability to track Agile progress and govern initiatives effectively.
- 1-2: Teams work in isolation, with limited leadership oversight or visibility into progress, risks, or portfolio health.
- 3-4: Governance frameworks are improving, providing leadership with growing visibility into performance, though gaps in consistency and reporting remain.
- 5: Leadership has comprehensive oversight of Agile performance, supported by governance frameworks that enable both autonomy and strategic alignment.
Dimension 3: Culture & collaboration
Examine how deeply Agile values are embedded in your organization’s culture and how effectively teams work together.
- 1-2: Agile practices are fragmented, limited to specific teams, with minimal cross-functional collaboration or leadership support for Agile principles.
- 3-4: Agile values are gaining traction, and collaboration between teams is improving, though cultural resistance and silos still exist.
- 5: Agile principles are fully embedded in the organizational culture, fostering seamless cross-functional collaboration and active leadership advocacy.
Dimension 4: Scalability
Evaluate your organization’s ability to scale Agile across teams, departments, and portfolios.
- 1-2: Agile practices are inconsistent, and scaling efforts are hindered by fragmented frameworks, tools, and leadership support.
- 3-4: Agile is beginning to scale, with early standardization efforts, though challenges in governance, tools, and alignment persist.
- 5: Agile is fully scalable, supported by standardized frameworks, tools, and processes that enable alignment and adaptability across the enterprise.
Scoring Guide
Whether you’re laying the groundwork for Agile adoption or optimizing at the enterprise level, targeted actions will help you address gaps and capitalize on opportunities for growth.
This section provides specific recommendations based on your maturity level.
If you scored 24–25 points: Enterprise Agile
You’re operating at the highest level of Agile maturity, with Agile practices embedded in your culture and strategy. To maintain this level and adapt to future challenges:
- Emphasize continuous improvement: Encourage teams to experiment and refine practices, ensuring processes stay efficient and innovative.
- Prepare for market evolution: Ensure your Agile frameworks remain adaptable to external changes, such as emerging technologies or shifts in market demands.
- Scale Agile innovations across the ecosystem: Extend Agile beyond your organization’s boundaries by fostering collaboration with partners, suppliers, or even customers. This ecosystem approach allows you to unlock additional value from existing relationships.
If you scored 15–23 points: Cross-Functional Agile
Your organization has made significant progress, but scaling Agile enterprise-wide requires deeper alignment and standardization. To advance:
- Align Agile with strategic objectives: Tighten the connection between Agile initiatives and business goals to enhance enterprise-wide impact.
- Refine governance and visibility: Enhance portfolio management practices with tools that provide real-time insights into performance and progress.
- Standardize frameworks: Ensure consistency across teams by adopting unified practices and tools, enabling scalability.
If you scored 10–14 points: Team-Level Agile
Your Agile practices are well-established at the team level but lack the strategic alignment and collaboration needed for broader impact. To progress:
- Foster collaboration: Break down silos and encourage cross-functional engagement to align team-level efforts with enterprise goals.
- Engage leadership: Build leadership buy-in by emphasizing Agile’s strategic value, ensuring active support for scaling initiatives.
- Develop governance and visibility: Introduce frameworks that provide leaders with visibility into Agile efforts while maintaining team autonomy.
If you scored below 10 points: Ad-hoc Agile
Your organization is in the early stages of Agile maturity. Agile practices are isolated, and there’s minimal alignment with broader business objectives. To build momentum:
- Establish strategic alignment: Connect Agile efforts to business goals, providing direction and purpose for teams.
- Invest in foundational tools: Adopt tools that offer visibility into team progress, allowing leadership to monitor and guide efforts effectively.
- Set up governance structures: Develop lightweight governance frameworks to oversee Agile initiatives without restricting team autonomy.
Speed of Agile transformation
The journey to Enterprise Agile varies widely depending on organizational readiness, leadership involvement, and cultural factors. On average, organizations may spend:
Ad-hoc to Team-Level Agile: 6–12 months
Team-Level to Cross-Functional Agile: 12–24 months
Cross-Functional to Enterprise Agile: 18–36 months
Several key factors can help accelerate this process:
Leadership commitment: Strong executive sponsorship ensures Agile initiatives are prioritized and aligned with strategic goals, reducing roadblocks.
The right tools and frameworks: Tools like Kiplot’s Agile Portfolio Management software enable organizations to improve visibility, governance, and alignment, making it easier to scale enterprise agility and manage complex portfolios effectively.
Culture of continuous improvement: Encouraging experimentation, collaboration, and regular feedback empowers teams to adapt and optimize faster, driving progress across maturity levels.
By focusing on these accelerators, your organization can significantly reduce the time required to achieve Enterprise Agile maturity.
Achieving Enterprise Agile
Reaching Enterprise Agile maturity requires deliberate focus and continuous effort. Large enterprises face challenges in aligning teams, scaling practices, and maintaining visibility across portfolios, but these barriers can be addressed with targeted actions and the right tools.
By assessing your current maturity level and prioritizing improvements in strategic alignment, governance, collaboration, and scalability, your organization can build the foundation for sustainable Agile transformation. Implementing frameworks and tools that provide clarity and consistency will enable your teams to deliver value efficiently while staying aligned with business priorities.
Learn more about how Kiplot’s enterprise Agile portfolio management software can support your organization in advancing its Agile maturity and achieving strategic goals.