Section 1: Introduction and Purpose
1.1 Objective
The Agile Transformation Playbook is designed to guide organizations through the process of adopting agile methodologies to become adaptable, and customer-centric enterprises. This playbook provides a structured approach to help leaders and teams transition from traditional project management practices to agile ways of working, driving enterprise agility at scale.
The objective of this playbook is to:
- Provide a Clear Roadmap: Outline a step-by-step process for implementing agile methodologies across the organization, from initial pilot projects to full-scale enterprise adoption.
- Align with Strategic Goals: Ensure that the agile transformation aligns with the organization's strategic objectives, delivering tangible business value and improving overall performance.
- Facilitate Cultural Change: Foster a culture of collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement, which are essential to successful agile adoption.
- Empower Leadership and Teams: Equip leaders, managers, and teams with the knowledge, tools, and best practices required to lead and sustain an agile transformation.
1.2 Scope
This playbook covers all aspects of agile transformation, including:
- Strategic Alignment: How to align agile practices with business goals and objectives.
- Organizational Readiness: Assessing the current state and preparing the organization for change.
- Agile Implementation: A detailed roadmap for adopting agile frameworks, building agile teams, and scaling agile practices across the organization.
- Portfolio Management: Strategies for agile portfolio management that ensure projects and initiatives align with strategic priorities.
- Continuous Improvement: Methods for measuring success, incorporating feedback, and continuously improving agile practices.
This playbook is intended for use by:
- C-suite Executives: Chief Information Officers (CIOs), Chief Technology Officers (CTOs), Chief Digital Officers (CDOs), Chief Operating Officers (COOs), Chief Transformation Officers, and Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) who are leading digital and agile transformations.
- Directors and Managers: Directors of PMO, Transformation, and Change Management, as well as Heads of Agile and Business Change.
- Agile Coaches and Transformation Managers: Enterprise Agile Coaches, Transformation Programme Managers, and other professionals responsible for driving agile adoption and fostering a culture of agility.
1.3 The Need for Agile Transformation
Organizations face increasing pressure to innovate rapidly, respond to market changes, and deliver value to customers faster than ever before. Traditional project management approaches, characterized by rigid structures and long planning cycles, often struggle to keep up with these demands.
Agile transformation provides a solution by:
- Enhancing Flexibility: Agile practices enable organizations to respond quickly to changing customer needs and market conditions, fostering a culture of adaptability.
- Accelerating Time to Market: By breaking work into smaller, manageable increments and emphasizing early and continuous delivery, agile methodologies reduce time to market.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction: Agile focuses on delivering customer value and incorporates regular feedback loops, ensuring that the end product meets customer needs.
- Driving Collaboration and Engagement: Agile promotes a collaborative work environment, where cross-functional teams work together towards common goals, leading to higher levels of engagement and job satisfaction.
Agile transformation is not just a change in process; it is a shift in mindset. It requires a commitment to continuous improvement, learning, and innovation. This playbook provides the guidance and tools necessary to embark on this journey and realize the full benefits of agile transformation.
1.4 How to Use This Playbook
This playbook is structured to be both a comprehensive guide and a practical resource:
- Step-by-Step Guidance: Follow the outlined phases and steps to implement agile transformation in a structured and systematic way.
- Tools and Templates: Utilize the provided tools, templates, and checklists to facilitate the agile transformation process.
- Best Practices: Learn from best practices and real-world examples to avoid common pitfalls and ensure success.
- Continuous Reference: Use this playbook as a continuous reference throughout your agile journey. Revisit sections as needed to refresh your understanding and adapt strategies to evolving business needs.
By following this playbook, organizations can navigate the complexities of agile transformation, drive sustainable change, and achieve strategic business objectives. Let’s begin the journey towards agility and innovation.
Section 2: Understanding Agile Transformation
2.1 What is Agile Transformation?
Agile Transformation is the process of shifting an organization’s structure, culture, and operations towards a more agile way of working. It involves adopting agile principles and methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean, to enhance flexibility, efficiency, and customer-centricity. This transformation is not just about implementing a set of practices or tools; it’s a fundamental shift in how the organization operates, collaborates, and delivers value.
Agile transformation is characterized by:
- Iterative Development: Breaking work into smaller, incremental pieces that are delivered in short cycles, allowing for continuous feedback and adaptation.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encouraging teams from different disciplines to work together, breaking down silos, and promoting knowledge sharing.
- Customer Focus: Prioritizing customer needs and delivering value early and often, ensuring that products and services meet real-world requirements.
- Continuous Improvement: Emphasizing regular reflection, learning, and adaptation to improve processes, products, and services continuously.
By embracing these principles, organizations can become more responsive to change, innovate faster, and create products and services that better meet customer needs.
2.2 Why Agile Transformation?
Organizations must be able to adapt quickly to survive and thrive. Traditional project management approaches, which often rely on long planning cycles, hierarchical decision-making, and rigid processes, can impede an organization's ability to respond to market changes and customer demands swiftly.
Agile transformation provides several key benefits:
- Increased Responsiveness: Agile organizations can quickly respond to changes in the market, customer feedback, and emerging opportunities. This adaptability is crucial in a world where customer preferences and technological advances can shift rapidly.
- Enhanced Innovation: By fostering a culture of experimentation and learning, agile transformation encourages innovation. Teams are empowered to try new ideas, learn from failures, and iterate quickly, leading to more innovative solutions and products.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Agile practices emphasize frequent delivery of valuable features and continuous engagement with customers. This ensures that the final product aligns with customer needs and provides a higher level of satisfaction.
- Greater Efficiency: Agile methodologies streamline workflows, eliminate waste, and reduce time to market. This results in more efficient use of resources and a higher return on investment.
- Employee Engagement: Agile promotes a collaborative and inclusive work environment, where team members have a voice in decision-making and are encouraged to take ownership of their work. This leads to higher levels of job satisfaction and employee engagement.
2.3 Agile Transformation vs. Agile Adoption
While the terms "agile transformation" and "agile adoption" are often used interchangeably, they refer to different levels of change within an organization:
- Agile Adoption: Refers to the implementation of agile practices and methodologies at the team level. It focuses on adopting specific agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban for project management and delivery. Agile adoption may be limited to certain teams or departments within the organization.
- Agile Transformation: Goes beyond the adoption of agile practices at the team level. It involves a holistic change in the organization's culture, mindset, structure, and processes. Agile transformation seeks to embed agility into the DNA of the organization, influencing how decisions are made, how work is prioritized, and how the organization interacts with its customers and stakeholders.
In essence, agile adoption is about doing agile, while agile transformation is about being agile. For a successful agile transformation, it is crucial to embrace both the practices and the underlying principles of agility.
2.4 Key Principles of Agile Transformation
To successfully navigate an agile transformation, organizations should adhere to the following key principles:
- Customer-Centricity: Place the customer at the center of everything. Prioritize delivering value that meets customer needs and continuously seek feedback to refine and improve offerings.
- Empowerment: Empower teams to make decisions and take ownership of their work. Foster an environment where team members feel valued and trusted to contribute to the organization’s goals.
- Transparency: Promote openness and transparency in communication, decision-making, and progress tracking. Use visual tools and regular check-ins to ensure everyone is aligned and informed.
- Adaptability: Embrace change and be willing to pivot when necessary. Use iterative processes to test ideas, gather feedback, and adjust course based on learnings.
- Collaboration: Encourage cross-functional collaboration to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise. Break down silos and promote teamwork across departments and functions.
- Continuous Improvement: Commit to a culture of learning and improvement. Regularly reflect on processes, celebrate successes, and identify areas for enhancement. Use retrospectives, feedback loops, and metrics to drive continuous improvement.
2.5 Real-World Examples of Agile Transformation
Agile transformation is being embraced by organizations across various industries. Here are a few real-world examples:
- Spotify: The music streaming giant is known for its unique agile methodology, often referred to as the "Spotify model." This approach focuses on autonomous squads, tribes, chapters, and guilds, enabling small teams to operate like startups within the organization. Spotify's agile transformation has allowed it to innovate rapidly, scale effectively, and stay ahead of the competition.
- ING Bank: The Dutch multinational bank underwent a significant agile transformation to enhance its customer experience and speed up innovation. ING adopted an agile approach across its entire organization, restructuring teams into agile squads and focusing on customer-driven development. This transformation has helped ING improve time-to-market for new products and services while maintaining high customer satisfaction.
- Airbnb: The home-sharing platform uses agile methodologies to iterate and improve its platform continuously. By focusing on customer feedback and using data-driven decision-making, Airbnb has been able to adapt quickly to market demands and enhance its user experience. Agile transformation has played a key role in Airbnb’s ability to scale and innovate.
2.6 The Role of Leadership in Agile Transformation
Leadership plays a crucial role in driving and sustaining agile transformation. For agile to be successfully adopted, leaders must:
- Champion Agility: Act as advocates for agile practices and principles. Leaders should model agile behaviors, support the agile vision, and encourage a culture of experimentation and learning.
- Provide Clear Direction: Align agile transformation efforts with the organization’s strategic goals. Leaders must ensure that teams understand the purpose behind the transformation and how it contributes to the overall success of the organization.
- Enable Teams: Remove obstacles that hinder agile adoption. Leaders should provide the necessary resources, tools, and training to empower teams to succeed. They should also create a safe environment where teams can take risks and learn from failures.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage collaboration across the organization. Leaders should break down silos, promote knowledge sharing, and facilitate cross-functional teamwork.
- Commit to Continuous Improvement: Embrace a mindset of continuous improvement. Leaders should regularly seek feedback, measure progress, and be willing to adjust strategies as needed to drive agility.
By understanding the principles of agile transformation and the pivotal role of leadership, organizations can lay a solid foundation for their agile journey. The following sections of this playbook will provide a detailed roadmap and practical steps for implementing agile transformation, enabling organizations to realize the full benefits of agility.
Section 3: Defining the Vision and Strategy
3.1 Setting the Vision
A successful agile transformation starts with a clear and compelling vision. This vision serves as a guiding star, aligning the organization’s efforts and inspiring commitment from all stakeholders. Without a shared vision, transformation initiatives risk becoming fragmented and losing momentum.
Key Elements of an Agile Transformation Vision:
- Customer-Centricity: The vision should emphasize the importance of delivering value to customers. It should highlight how agility will enable the organization to better understand and respond to customer needs, resulting in superior products and services.
- Adaptability and Speed: The vision should focus on building a responsive organization that can quickly adapt to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities. It should convey the need for faster time-to-market and the ability to pivot when necessary.
- Empowerment and Collaboration: The vision should underscore the importance of empowering teams and fostering a culture of collaboration. It should advocate for breaking down silos and enabling cross-functional teamwork.
- Continuous Improvement: The vision should commit to a culture of continuous learning and improvement. It should encourage experimentation, innovation, and the regular reflection needed to enhance processes and outcomes.
Creating the Vision Statement:
A vision statement should be concise, inspirational, and aligned with the organization's broader strategic objectives. Here is an example of a vision statement for agile transformation:
"To become a customer-centric, innovative, and adaptable organization that delivers exceptional value by empowering our teams, embracing change, and continuously improving our ways of working."
This vision statement can be customized to reflect the specific context and goals of the organization. It should be communicated widely and consistently to ensure all employees understand and are inspired by the transformation journey.
3.2 Strategic OKRs
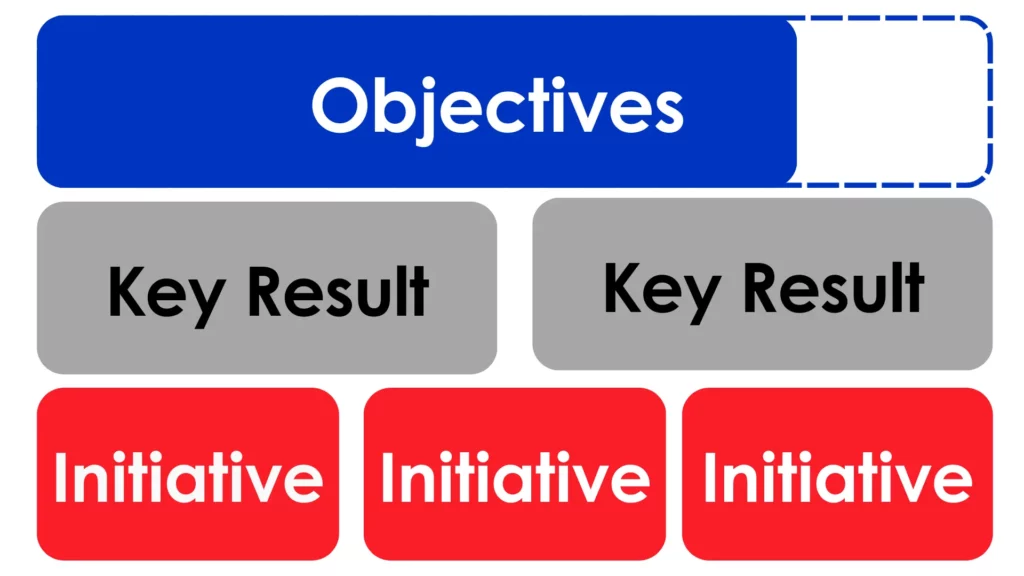
Once the vision is set, defining clear and measurable OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) is essential to guide the agile transformation process. OKRs help align the organization around its strategic goals and provide a framework for measuring progress and success.
What are OKRs?
OKRs, or Objectives and Key Results, are a goal-setting framework that helps organizations define and track measurable outcomes. The Objective is a clear, aspirational goal that sets a strategic direction. Key Results are the specific, measurable milestones that track progress toward achieving the objective. Together, OKRs ensure that every level of the organization is focused on the most important initiatives and that success can be quantified.
- Objective: The overarching, qualitative goal you aim to achieve.
- Key Results: The measurable outcomes that indicate how well you are progressing toward the objective.
OKRs are particularly well-suited for agile transformation, as they foster transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement—core principles of agility.
image:medium
Examples of Strategic OKRs for Agile Transformation:
- Objective: Increase Speed to Market
Key Results:
- Reduce the time required to deliver new products or features by 50% within the next 12 months.
- Shorten the average product release cycle from 6 months to 3 months.
- Increase the percentage of on-time project deliveries from 60% to 90%.
- Objective: Enhance Customer Satisfaction
Key Results:
- Improve customer satisfaction scores (e.g., Net Promoter Score) by 20% over the next 6 months.
- Increase the frequency of product releases that incorporate customer feedback by 50%.
- Achieve a 30% reduction in customer-reported issues within 9 months.
- Objective: Improve Team Productivity
Key Results:
- Increase team productivity by 30% by reducing bottlenecks and empowering teams with agile tools.
- Decrease dependency wait times between teams by 40%.
- Increase the number of sprints completed with no roll-over tasks from 50% to 80%.
- Objective: Foster Innovation
Key Results:
- Launch 5 new innovative projects within the next year, leveraging agile methodologies to test and iterate quickly.
- Allocate 20% of team capacity for experimentation and innovative initiatives.
- Generate 10 new customer-driven feature ideas within 6 months through innovation workshops.
- Objective: Embed a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Key Results:
- Implement regular retrospectives and feedback loops in 100% of agile teams within the next 3 months.
- Ensure that 90% of action items from retrospectives are resolved within the next sprint.
- Increase participation in continuous learning and improvement programs by 50%.
Creating Effective OKRs
When setting Objectives and Key Results (OKRs), it's essential to ensure that each objective and its corresponding key results are structured in a way that drives focus and measurable progress. Effective OKRs should meet specific criteria to ensure they are impactful and aligned with the organization’s overall goals. To achieve this, OKRs can be guided by similar principles to the SMART framework, ensuring they are well-defined and actionable.
- Specific: The Objective should be clear and focused on a specific strategic area. Each Key Result should be precise, outlining exactly what needs to be accomplished to achieve the objective.
Example:
Objective: Increase Speed to Market
Key Result: Reduce time to deliver new products by 50%.
- Measurable: Key Results should be quantitative and measurable, allowing progress to be tracked over time. This ensures that you can determine how far along you are toward achieving the objective.
Example:
Key Result: Improve customer satisfaction scores by 20%.
- Achievable: While OKRs are meant to be ambitious, they should also be attainable with the available resources and within the current business context. Stretch goals are encouraged, but they must remain realistic.
Example:
Key Result: Launch 5 innovative projects leveraging agile methodologies within the next year.
- Relevant: Objectives must align with the organization’s broader strategic priorities. Each key result should directly contribute to achieving the objective and add value to the overall business strategy.
Example:
Objective: Improve Team Productivity (aligned with the broader goal of operational efficiency).
- Time-bound: Every OKR should have a defined timeframe within which the objective and key results are expected to be achieved. This creates urgency and helps maintain focus.
Example:
Key Result: Achieve a 30% increase in team productivity within the next 6 months.
By following these principles when creating OKRs, you ensure that your agile transformation efforts remain focused, measurable, and aligned with your organization’s long-term vision. OKRs provide clarity on what needs to be achieved and create a structured path toward success.
Click here to read our full guide on how to craft enterprise OKRs.
3.3 Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders is critical to the success of any agile transformation. Stakeholders include anyone who has a vested interest in the transformation or can influence its success. This often includes executives, managers, team leaders, and employees from various departments.
Steps to Effective Stakeholder Engagement:
- Identify Key Stakeholders: List all stakeholders who will be affected by the agile transformation or who have influence over its success. This may include executives, department heads, project managers, product owners, and team members.
- Understand Their Perspectives: Gather insights into stakeholders' concerns, expectations, and goals regarding the transformation. Conduct interviews, surveys, or workshops to understand their needs and apprehensions.
- Communicate the Vision and Goals: Share the agile transformation vision and strategic goals with stakeholders. Ensure they understand how the transformation aligns with the organization’s broader objectives and the benefits it will bring.
- Involve Stakeholders Early: Engage stakeholders early in the transformation process. Involve them in planning, decision-making, and setting priorities. Early involvement fosters ownership and commitment.
- Provide Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed of progress, challenges, and successes throughout the transformation journey. Regular updates build trust and keep stakeholders aligned and engaged.
- Address Concerns and Resistance: Be prepared to address any concerns or resistance to change. Listen actively to stakeholder feedback, provide clear answers, and offer support to ease the transition.
Communication Strategy:
Developing a robust communication strategy is vital to maintaining stakeholder engagement. The strategy should include:
- Communication Channels: Utilize various channels (e.g., emails, newsletters, town hall meetings, intranet, agile forums) to reach all stakeholders.
- Frequency: Determine how often updates and communications will be shared (e.g., weekly updates, monthly town halls).
- Content: Tailor the content to the audience. For example, executives may need high-level summaries, while team members may require detailed guidance.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for stakeholders to provide feedback, ask questions, and voice concerns.
3.4 Communicating the Why
To gain buy-in and commitment, it is crucial to communicate the “why” behind the agile transformation. People are more likely to support change if they understand its purpose and the benefits it brings.
Key Messages to Communicate:
- Alignment with Strategy: Explain how agile transformation aligns with the organization’s strategic goals. For example, if the company aims to become more customer-focused, highlight how agile practices will enable faster responses to customer needs.
- Business Benefits: Articulate the business benefits of agile transformation, such as increased efficiency, faster time-to-market, and improved innovation.
- Employee Benefits: Emphasize how agile transformation will benefit employees, including opportunities for greater empowerment, collaboration, and professional growth.
- Market and Industry Trends: Highlight market and industry trends that necessitate the adoption of agile practices. For instance, discuss how competitors are leveraging agility to gain a competitive edge or how customer expectations are evolving.
- Examples and Stories: Use real-world examples and success stories to illustrate the positive impact of agile transformation. Share case studies from similar organizations or success stories from within the company.
Leadership's Role in Communicating the Why:
Leaders play a pivotal role in communicating the purpose of the transformation. They should:
- Lead by Example: Demonstrate commitment to agile principles through their actions and decisions.
- Be Transparent: Be honest about the challenges and opportunities of the transformation.
- Be Visible: Actively participate in communication efforts, attend meetings, and engage with teams.
- Be Supportive: Offer support and resources to teams and individuals as they navigate the transformation.
By clearly defining the vision, setting strategic goals, engaging stakeholders, and effectively communicating the purpose of the agile transformation, organizations can build a strong foundation for their agile journey. This foundation will help ensure that the transformation is not just a temporary change but a sustainable shift towards agility, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
Section 4: Assessing the Current State
4.1 Organizational Readiness Assessment
Before embarking on an agile transformation, it is essential to understand the current state of the organization. This includes assessing readiness for change, identifying existing capabilities, and recognizing potential challenges. A thorough assessment will provide a baseline that helps to tailor the transformation approach to the organization's specific needs.
Key Objectives of the Organizational Readiness Assessment:
- Understand Current Practices: Gain insights into the existing project management practices, workflows, and processes.
- Gauge Cultural Readiness: Assess the organizational culture, including openness to change, collaboration, and innovation.
- Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: Recognize existing strengths that can be leveraged and weaknesses that need to be addressed.
- Assess Leadership Support: Evaluate the level of support and commitment from leadership and key stakeholders.
- Understand Resistance Points: Identify potential areas of resistance and concerns that may hinder the transformation.
Methods for Conducting the Readiness Assessment:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Develop and distribute surveys to gather insights from employees, managers, and leaders. Focus on areas such as current project management practices, perceptions of agile, readiness for change, and potential challenges.
- Interviews and Workshops: Conduct one-on-one interviews and interactive workshops with key stakeholders. These sessions provide a deeper understanding of individual perspectives, concerns, and aspirations regarding agile transformation.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus group discussions with representatives from different departments and teams. Focus groups encourage open dialogue and help uncover common themes and challenges.
- Maturity Assessment Tools: Use agile maturity assessment tools to evaluate the current state of agile practices within the organization. Tools like the Agile Maturity Model can provide a structured framework for assessing agility across various dimensions.
- Observation: Observe existing workflows, meetings, and team interactions. This helps to understand how work is currently done and identify areas where agile practices can add value.
Key Areas to Assess:
- Leadership Commitment: Evaluate the commitment and support from executive leadership. Assess whether leaders are willing to champion agile principles and provide the necessary resources.
- Cultural Alignment: Assess whether the organization's culture supports values such as collaboration, transparency, and adaptability. Identify cultural barriers that may need to be addressed.
- Current Processes and Workflows: Map out existing project management processes, workflows, and methodologies. Identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas where agile can improve outcomes.
- Team Dynamics: Evaluate team structures, roles, and dynamics. Assess how well teams collaborate and whether they are empowered to make decisions.
- Technology and Tools: Review the current technology stack and tools used for project management and collaboration. Identify gaps and opportunities for integrating agile tools.
- Skills and Competencies: Assess the current skill levels and competencies related to agile methodologies. Identify training needs and areas for skill development.
4.2 Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities
Understanding the pain points and opportunities within the organization is crucial for designing a targeted and effective agile transformation strategy. By identifying areas that need improvement and potential quick wins, organizations can prioritize efforts and achieve early successes that build momentum.
Common Pain Points:
- Siloed Departments: Lack of collaboration between departments, leading to communication breakdowns and inefficiencies.
- Slow Decision-Making: Bureaucratic processes that delay decision-making and hinder responsiveness.
- Resistance to Change: Employees or managers who are resistant to adopting new ways of working due to fear, uncertainty, or comfort with the status quo.
- Inefficient Processes: Outdated or rigid processes that slow down project delivery and reduce flexibility.
- Lack of Customer Focus: Projects that are not aligned with customer needs or lack regular customer feedback, leading to products that do not meet market demands.
- Low Employee Engagement: Teams that feel disengaged or lack a sense of ownership and empowerment.
Identifying Opportunities:
- Quick Wins: Identify areas where agile practices can be introduced with minimal disruption and deliver immediate value. Quick wins help build credibility and support for the transformation.
- High-Impact Areas: Focus on areas that have a significant impact on the organization’s strategic goals, such as customer-facing projects or critical product development initiatives.
- Existing Agile Practices: Identify teams or departments that are already using agile practices, even informally. These teams can serve as role models and help drive broader adoption.
- Innovative Projects: Look for projects that require innovation and adaptability. Agile methodologies are particularly well-suited to projects with high uncertainty and evolving requirements.
- Employee Champions: Identify employees who are enthusiastic about agile and can act as champions. These individuals can help advocate for agile practices and influence their peers.
4.3 Mapping the Current State
To create a clear understanding of the current state, it's helpful to visualize the organization's structure, processes, and workflows. Mapping the current state provides a baseline for planning the transformation and identifying areas for improvement.
Steps to Map the Current State:
- Process Mapping: Create detailed process maps of how work currently flows through the organization. Include key steps, decision points, roles involved, and tools used. Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Value Stream Mapping: Use value stream mapping to visualize how value is delivered to the customer. Identify value-adding and non-value-adding activities, and highlight areas where agile practices can increase efficiency and reduce waste.
- Organizational Structure: Map the current organizational structure, including departments, teams, and reporting lines. Identify silos and areas where collaboration can be improved.
- Stakeholder Map: Create a stakeholder map to identify key stakeholders, their roles, and their influence on the agile transformation. Understand their expectations and concerns.
- Technology Landscape: Map the existing technology landscape, including project management tools, communication platforms, and collaboration software. Identify gaps and areas where agile tools can be integrated.
- Cultural Map: Develop a cultural map to understand the prevailing organizational culture, values, and behaviors. Identify cultural attributes that align with agile principles and areas that may need cultural change.
4.4 Analyzing the Findings
Once the current state has been assessed and mapped, analyze the findings to draw meaningful insights. This analysis will inform the design of the agile transformation strategy and help prioritize actions.
Key Questions to Consider:
- What are the major barriers to agility in the current state?
- Where are the opportunities for quick wins and high-impact improvements?
- How ready is the organization, culturally and structurally, for agile transformation?
- What are the key strengths that can be leveraged to drive agile adoption?
- Which stakeholders are most supportive, and who may require additional engagement?
- What changes to processes, tools, and roles are necessary to support agile practices?
Creating a Current State Report:
Summarize the findings from the assessment in a current state report. This report should include:
- A summary of the current project management practices and workflows.
- Key pain points and areas for improvement.
- Identified opportunities and quick wins.
- Cultural and organizational readiness for agile transformation.
- Stakeholder insights and potential resistance points.
- Recommendations for next steps based on the analysis.
This current state report will serve as a foundation for developing a tailored agile transformation strategy that addresses the organization’s specific needs and challenges.
4.5 Gaining Buy-In from Leadership
Gaining buy-in from leadership is critical to the success of the agile transformation. Leaders set the tone for the organization and play a pivotal role in championing change. Use the findings from the readiness assessment to make a compelling case for agile transformation.
Steps to Gain Leadership Buy-In:
- Present the Current State: Share the findings of the readiness assessment with leadership. Highlight key pain points, opportunities, and the need for change.
- Link to Strategic Goals: Connect the agile transformation to the organization’s strategic goals. Demonstrate how agility will help achieve business objectives such as faster innovation, improved customer satisfaction, and increased efficiency.
- Show the Benefits: Use data and examples to illustrate the benefits of agile transformation. Highlight success stories from other organizations and potential outcomes for the company.
- Address Concerns: Be prepared to address any concerns or objections. Provide evidence-based responses and offer solutions to mitigate risks.
- Propose a Plan: Present a high-level agile transformation plan, including key phases, timelines, and resource requirements. Show that there is a structured approach to managing the transformation.
- Request Support: Clearly outline the support needed from leadership, including commitment, resources, and active participation. Emphasize the importance of leadership involvement in driving the transformation.
By thoroughly assessing the current state and gaining leadership buy-in, organizations can lay a strong foundation for their agile transformation journey. The insights gained from this assessment will guide the development of a tailored strategy that addresses the unique challenges and opportunities of the organization, ensuring a successful transition to agility.
Section 5: Designing the Transformation Roadmap
5.1 The Phased Approach to Agile Transformation
An agile transformation is a complex journey that requires a structured and phased approach. By breaking the transformation into manageable phases, organizations can gradually implement changes, learn from each step, and adjust the course as needed. A phased approach helps minimize disruption, manage risks, and build momentum through early successes.
Overview of the Phases:
- Phase 1: Pilot Projects
- Focus: Test agile practices in a controlled environment to demonstrate value and learn from experience.
- Activities: Select pilot projects, form agile teams, train team members, implement agile ceremonies, and measure initial outcomes.
- Phase 2: Scaling Agile
- Focus: Expand agile practices beyond the pilot projects to additional teams and departments.
- Activities: Implement scaling frameworks (e.g., SAFe), align agile practices across teams, integrate agile into portfolio management, and refine processes based on feedback.
- Phase 3: Enterprise-Wide Adoption
- Focus: Embed agile practices across the entire organization and align all projects and initiatives with agile principles.
- Activities: Establish an Agile Center of Excellence (CoE), adapt governance and leadership practices, ensure alignment with strategic objectives, and cultivate a culture of continuous improvement.
5.2 Phase 1: Pilot Projects
The first phase of the transformation focuses on testing and validating agile practices through pilot projects. This phase provides an opportunity to learn, demonstrate value, and build a foundation for scaling agile across the organization.
Steps to Implement Pilot Projects:
- Select Pilot Projects:
- Choose 2-3 projects to serve as pilots for agile practices. Select projects that are of manageable size, have clear objectives, and can deliver value quickly.
- Criteria for selection may include cross-functional collaboration requirements, customer involvement, high visibility, or projects that are strategic priorities.
- Form Agile Teams:
- Assemble cross-functional, self-organizing teams for the pilot projects. Teams should include members from various disciplines required to deliver the project, such as developers, testers, designers, and business analysts.
- Define roles such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and team members. Ensure team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Train and Coach Teams:
- Provide training on agile principles, methodologies (e.g., Scrum, Kanban), and specific practices to be used in the pilot projects.
- Assign experienced agile coaches to guide the teams and provide ongoing support. Coaches help teams adopt agile practices, facilitate agile ceremonies, and overcome challenges.
- Implement Agile Ceremonies:
- Introduce key agile ceremonies, such as daily stand-ups, sprint planning, program increment (pi) planning, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. These ceremonies help teams collaborate, plan work, review progress, and continuously improve.
- Ensure that ceremonies are time-boxed, focused, and involve all team members.
- Measure Outcomes:
- Define metrics to measure the success of the pilot projects. Metrics may include lead time, cycle time, team velocity, customer satisfaction, and quality of deliverables.
- Collect feedback from team members and stakeholders to understand what is working well and what needs improvement.
- Document Learnings:
- Capture lessons learned from the pilot projects. Identify successes, challenges, and areas for improvement.
- Use these learnings to refine agile practices and prepare for scaling agile across more teams.
Expected Outcomes:
- Demonstration of the value of agile practices in real-world projects.
- Initial successes that build momentum and support for agile transformation.
- Insights and lessons learned that inform the next phase of the transformation.
5.3 Phase 2: Scaling Agile
The second phase focuses on scaling agile practices from pilot projects to more teams and departments. This phase requires establishing structures and frameworks that support agility at scale and ensure alignment across the organization.
Steps to Scale Agile:
- Implement Scaling Frameworks:
- Choose a scaling framework that fits the organization’s needs, such as Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), Large Scale Scrum (LeSS), or Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD).
- Implement the framework across multiple teams to ensure consistency in agile practices and alignment with strategic objectives.
- Expand Agile Teams:
- Form additional agile teams to work on new projects or initiatives. Ensure that these teams have the necessary skills and support to adopt agile practices.
- Maintain cross-functional collaboration and self-organization as core principles of agile teams.
- Align Agile Practices:
- Standardize agile practices across teams to ensure consistency and alignment. Define common practices, tools, and templates that all teams should use.
- Encourage teams to share best practices, experiences, and learnings through communities of practice or agile forums.
- Integrate Agile with Portfolio Management:
- Align agile practices with portfolio management to ensure that projects and initiatives support strategic objectives. Use agile portfolio management to prioritize projects based on value delivery, risk, and alignment with business goals.
- Implement lean portfolio management techniques to optimize resource allocation and reduce waste.
- Enhance Communication and Collaboration:
- Foster collaboration between teams to ensure alignment and coordination. Use agile ceremonies, such as scrum of scrums or program increment (PI) planning, to facilitate communication.
- Leverage tools and technology to support collaboration, transparency, and visibility across teams.
- Refine Processes Based on Feedback:
- Continuously collect feedback from teams and stakeholders to understand what is working well and where improvements are needed.
- Use retrospectives, feedback loops, and metrics to drive continuous improvement and refine agile practices.
Expected Outcomes:
- Successful scaling of agile practices to multiple teams and departments.
- Improved alignment and coordination across teams.
- Enhanced ability to respond to changing customer needs and market conditions.
5.4 Phase 3: Enterprise-Wide Adoption
The final phase involves embedding agile practices throughout the organization, ensuring that agility is integrated into the organizational culture, governance, and strategic decision-making.
Steps to Achieve Enterprise-Wide Adoption:
- Establish an Agile Center of Excellence (CoE):
- Create an Agile CoE to provide ongoing support, training, and governance for agile practices. The CoE acts as a central hub for agile expertise, resources, and best practices.
- Define the roles and responsibilities of the CoE, including coaching teams, developing training programs, and standardizing agile practices.
- Adapt Governance and Leadership Practices:
- Align governance and leadership practices with agile principles. Shift from traditional command-and-control structures to servant leadership and empowerment.
- Redefine leadership roles to support agile teams, remove obstacles, and facilitate decision-making.
- Ensure Alignment with Strategic Objectives:
- Integrate agile practices with the organization’s strategic planning and execution processes. Ensure that all projects and initiatives are aligned with strategic goals and deliver value.
- Use OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) to set clear goals and measure progress.
- Cultivate a Culture of Continuous Improvement:
- Promote a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encourage teams to experiment, take calculated risks, and learn from failures.
- Use regular retrospectives, feedback loops, and performance metrics to identify areas for improvement and drive innovation.
- Sustain Momentum:
- Celebrate successes and recognize achievements to maintain momentum and morale. Share success stories and case studies to demonstrate the impact of agile transformation.
- Continuously engage with stakeholders to keep them informed and involved in the transformation journey.
- Monitor and Adapt:
- Regularly monitor the progress of agile transformation and measure outcomes against defined goals. Use metrics such as time-to-market, customer satisfaction, team engagement, and innovation rates.
- Be prepared to adapt the transformation strategy based on feedback, lessons learned, and changing business needs.
Expected Outcomes:
- Agile practices are embedded across the organization, becoming the standard way of working.
- Increased alignment between strategy, execution, and value delivery.
- A culture of agility, adaptability, and continuous improvement is established.
5.5 Creating the Transformation Timeline
Developing a realistic timeline for the agile transformation is crucial for managing expectations, tracking progress, and ensuring accountability. The timeline should outline key phases, milestones, and deliverables for each phase of the transformation.
Steps to Create the Transformation Timeline:
- Define Key Milestones:
- Identify key milestones for each phase of the transformation, such as the launch of pilot projects, scaling of agile practices, establishment of the Agile CoE, and enterprise-wide adoption.
- Set Timeframes:
- Establish timeframes for each phase of the transformation. Consider factors such as the organization’s readiness, available resources, and the complexity of the transformation.
- Allocate Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for each phase, including personnel, training, tools, and technology. Ensure that resources are allocated appropriately to support the transformation.
- Monitor Progress:
- Use the timeline to monitor progress and track the completion of milestones. Regularly review the timeline and adjust as needed based on feedback and changing priorities.
- Communicate the Timeline:
- Share the transformation timeline with stakeholders to keep them informed and engaged. Ensure that everyone understands the phases, milestones, and expected outcomes.
Sample Transformation Timeline:
- Months 1-3: Conduct readiness assessment, select pilot projects, form agile teams, provide training, and launch pilot projects.
- Months 4-6: Complete pilot projects, measure outcomes, document learnings, refine agile practices, and begin scaling to additional teams.
- Months 7-12: Implement scaling frameworks, expand agile teams, integrate agile with portfolio management, and enhance collaboration.
- Months 13-18: Establish Agile CoE, adapt governance practices, align with strategic objectives, and promote continuous improvement.
- Months 19-24: Achieve enterprise-wide adoption, sustain momentum, monitor progress, and adapt the transformation strategy as needed.
5.6 Adapting the Roadmap Based on Feedback
Agile transformation is a journey of continuous learning and adaptation. The transformation roadmap should be flexible and responsive to feedback, allowing the organization to make adjustments as needed.
Steps to Adapt the Roadmap:
- Collect Feedback: Regularly gather feedback from teams, stakeholders, and customers. Use surveys, interviews, retrospectives, and other feedback mechanisms to understand what is working well and where improvements are needed.
- Analyze Data: Analyze data and metrics to assess the effectiveness of agile practices and the progress of the transformation. Look for trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Adjust Strategies: Based on feedback and data analysis, adjust the transformation strategies, timelines, and actions. Be open to changing course if necessary to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Communicate Changes: Clearly communicate any changes to the roadmap to stakeholders. Explain the rationale behind the changes and how they will contribute to the success of the transformation.
- Continue Learning: Embrace a mindset of continuous learning and improvement. Use each phase of the transformation as an opportunity to learn, adapt, and refine agile practices.
By designing a structured and phased transformation roadmap, organizations can navigate the complexities of agile transformation, manage risks, and achieve sustainable change. The roadmap provides a clear path forward, guiding the organization towards becoming a more agile, innovative, and customer-centric enterprise.
Section 6: Building Agile Teams and Culture
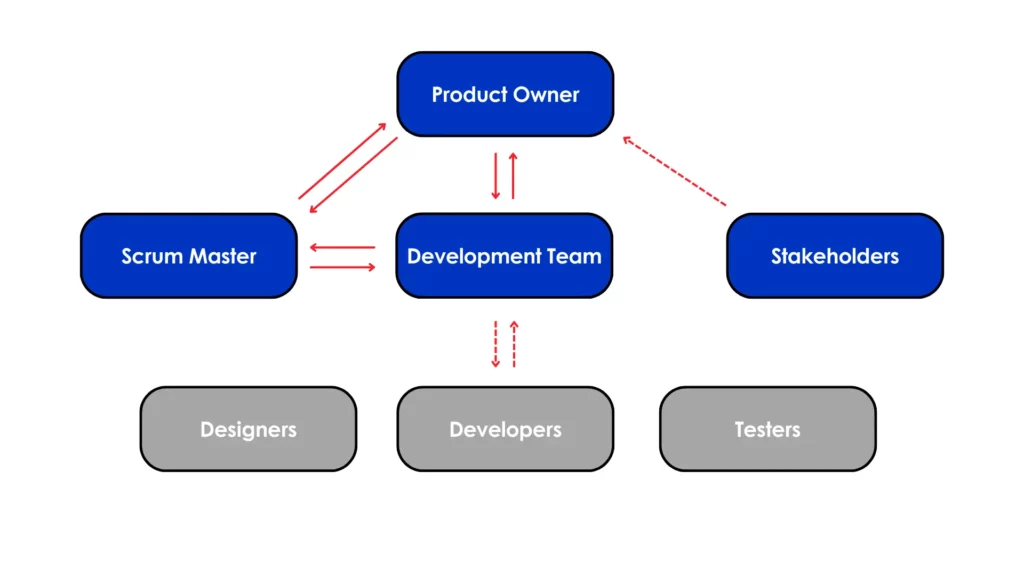
6.1 Forming Agile Teams
The foundation of a successful agile transformation lies in building agile teams that are empowered, cross-functional, and self-organizing. Agile teams are the engines of innovation and value delivery within an organization. They take ownership of their work, collaborate effectively, and continuously seek to improve.
image:medium
Key Characteristics of Agile Teams:
- Cross-Functional: Agile teams should consist of members with diverse skills and expertise, including development, testing, design, business analysis, and more. This ensures that the team can complete tasks from start to finish without relying on external resources.
- Self-Organizing: Agile teams are empowered to make decisions about how they work, how they organize themselves, and how they approach tasks. They take responsibility for their own processes and outcomes.
- Collaborative: Team members work closely together, share knowledge, and support each other to achieve common goals. Collaboration is key to solving problems quickly and delivering high-quality results.
- Empowered: Agile teams are given the autonomy to make decisions, experiment, and innovate. They have the authority to choose how to accomplish their objectives and are trusted to deliver results.
- Small and Stable: Agile teams are typically small (5-9 members) to facilitate effective communication and collaboration. Teams should be stable enough to develop strong working relationships and collective ownership over time.
Steps to Form Agile Teams:
- Identify Required Skills: Determine the skills and expertise needed to complete the project or deliver the product. Include members from different disciplines to ensure a balanced team.
- Assemble the Team: Form teams by selecting members with the necessary skills and a willingness to embrace agile principles. Ensure that the team has a mix of technical and business knowledge.
- Define Roles: Clearly define roles within the team, such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and team members. While roles are defined, the team should maintain flexibility and collaboration.
- Foster Team Identity: Encourage teams to create their own identity, including team names, goals, and working agreements. A strong team identity fosters ownership and motivation.
- Provide Training and Support: Offer training on agile principles, methodologies, and tools to help team members understand their roles and responsibilities. Provide ongoing coaching and support to help teams thrive.
6.2 Creating a Collaborative Culture
A successful agile transformation requires more than just forming agile teams; it also demands a shift in organizational culture. Creating a culture that supports collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement is essential for sustaining agility.
Key Elements of a Collaborative Agile Culture:
- Transparency: Open and honest communication is vital. Teams should share information freely, provide visibility into progress and challenges, and ensure that everyone is aligned.
- Trust: Build a culture of trust where team members feel safe to express their ideas, take risks, and make mistakes. Trust fosters innovation and encourages experimentation.
- Empowerment: Empower teams to make decisions and take ownership of their work. Provide the autonomy and resources they need to succeed, and remove obstacles that hinder their progress.
- Continuous Feedback: Encourage regular feedback loops within and across teams. Feedback helps teams learn, improve, and adapt. Use retrospectives, reviews, and informal feedback sessions to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
- Collaboration: Break down silos and promote cross-functional collaboration. Encourage teams to work together, share knowledge, and leverage each other’s strengths. Use agile ceremonies and tools to facilitate collaboration.
- Respect and Inclusion: Create an inclusive environment where diverse perspectives are valued and respected. Encourage participation from all team members and recognize their contributions.
Building a Collaborative Culture:
- Lead by Example: Leadership should model the behaviors they want to see. Demonstrate transparency, trust, and empowerment in your actions and decisions.
- Promote Open Communication: Encourage open communication across all levels of the organization. Use tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Confluence to facilitate communication and information sharing.
- Encourage Cross-Functional Teams: Form cross-functional teams that bring together members from different departments and areas of expertise. This encourages collaboration and a holistic approach to problem-solving.
- Provide Training: Offer training on communication, collaboration, and feedback skills. Equip team members with the tools and techniques to work effectively together.
- Celebrate Collaboration: Recognize and celebrate examples of effective collaboration. Highlight stories of teamwork and collective success to reinforce the value of collaboration.
6.3 Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a core principle of agile, and fostering this mindset is critical for achieving sustainable success. A culture of continuous improvement encourages teams to reflect on their work, learn from their experiences, and make incremental improvements over time.
Key Practices for Continuous Improvement:
- Retrospectives: Regular retrospectives provide teams with the opportunity to reflect on their work, identify what went well, and discuss areas for improvement. Retrospectives should result in actionable items that the team commits to implementing in the next iteration.
- Kaizen Mindset: Adopt a Kaizen mindset, which emphasizes small, continuous improvements rather than large, disruptive changes. Encourage teams to look for ways to optimize their processes and work incrementally.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops to gather insights from customers, stakeholders, and team members. Use this feedback to make data-driven decisions and adjust the course as needed.
- Experimentation: Encourage teams to experiment with new ideas, practices, and tools. Create a safe environment where failure is seen as a learning opportunity. Document learnings and share them with other teams.
- Metrics and Measurement: Use metrics to track performance, measure progress, and identify areas for improvement. Metrics such as cycle time, lead time, defect rates, and customer satisfaction provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of agile practices.
Promoting Continuous Improvement:
- Create a Safe Environment: Build an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing feedback, admitting mistakes, and proposing new ideas. Psychological safety is key to fostering continuous improvement.
- Provide Resources: Offer resources and tools that support continuous improvement, such as training, workshops, and access to industry best practices. Encourage teams to stay informed about new trends and techniques.
- Set Improvement Goals: Encourage teams to set specific, measurable goals for improvement. These goals should be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and reviewed regularly.
- Recognize Improvement Efforts: Acknowledge and reward teams for their efforts to improve processes, innovate, and achieve better outcomes. Recognition reinforces the importance of continuous improvement.
6.4 Overcoming Cultural Challenges
Transforming the organizational culture to support agile practices may face resistance and challenges. Addressing these challenges proactively is essential to building a sustainable agile culture.
Common Cultural Challenges and Solutions:
- Resistance to Change: Resistance may arise from fear of the unknown, comfort with existing processes, or concerns about job security.
- Solution: Communicate the benefits of agile transformation clearly. Involve employees in the process, listen to their concerns, and provide support to ease the transition.
- Siloed Mindset: Traditional organizational structures and departments may create silos that hinder collaboration.
- Solution: Break down silos by forming cross-functional teams, encouraging collaboration across departments, and promoting a shared vision and goals.
- Lack of Trust: Trust issues can arise due to past experiences, hierarchical structures, or lack of transparency.
- Solution: Build trust by promoting transparency, encouraging open communication, and demonstrating commitment to agile principles. Empower teams to make decisions and take ownership.
- Fear of Failure: A fear of failure may discourage teams from experimenting and innovating.
- Solution: Foster a safe environment where failure is seen as a learning opportunity. Encourage experimentation, provide support, and celebrate learning from mistakes.
- Limited Buy-In: Lack of buy-in from leadership or key stakeholders can impede cultural change.
- Solution: Secure leadership commitment by demonstrating the value of agile transformation. Involve leaders in the transformation process, provide training, and communicate success stories.
6.5 Scaling Agile Culture Across the Organization
As agile practices are scaled across the organization, it is essential to ensure that the agile culture is also scaled. Consistency in cultural values and behaviors supports effective collaboration and alignment.
Strategies for Scaling Agile Culture:
- Agile Champions: Identify and empower agile champions who can advocate for agile practices, share best practices, and support other teams. Champions help to spread the agile mindset and foster a culture of collaboration.
- Communities of Practice: Establish communities of practice where agile practitioners can come together to share knowledge, experiences, and best practices. These communities create a sense of belonging and collective learning.
- Agile Training and Development: Offer ongoing training and development programs focused on agile principles, collaboration, and leadership. Continuous learning reinforces agile culture and equips employees with the skills needed to succeed.
- Consistent Messaging: Ensure that messaging about agile principles, values, and behaviors is consistent across the organization. Use internal communication channels, newsletters, and events to reinforce the agile culture.
- Leadership Alignment: Align leadership practices with agile values. Leaders should model agile behaviors, support teams, and promote a culture of continuous improvement.
- Recognition and Rewards: Recognize and reward behaviors that align with the agile culture. Celebrate examples of collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement to reinforce the desired cultural values.
By building agile teams, creating a collaborative culture, fostering continuous improvement, overcoming cultural challenges, and scaling agile culture across the organization, companies can create an environment that supports agility, innovation, and sustained success. This cultural foundation is critical for realizing the full benefits of agile transformation and achieving long-term business objectives.
Section 7: Implementing Agile Practices and Tools
7.1 Choosing the Right Agile Framework
One of the first steps in implementing agile practices is selecting the appropriate agile framework that best suits the organization's needs, culture, and project requirements. Different frameworks offer various approaches to managing workflows, teams, and projects, and the choice will influence how agile principles are operationalized within the organization.
Common Agile Frameworks:
- Scrum:
- Overview: Scrum is a popular agile framework that focuses on iterative development, team collaboration, and delivering high-value products. It is structured around sprints, which are time-boxed iterations typically lasting 2-4 weeks.
- Key Roles: Scrum Master, Product Owner, Development Team.
- Key Ceremonies: Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective.
- Best For: Projects with complex requirements that can benefit from regular feedback and adjustments.
- Kanban:
- Overview: Kanban is a visual workflow management method that emphasizes continuous delivery, limiting work in progress, and optimizing flow. It uses a Kanban board to visualize tasks and track their progress.
- Key Elements: Kanban Board, Work in Progress (WIP) Limits, Continuous Flow.
- Best For: Teams looking for flexibility and incremental improvement without the need for fixed iterations or sprints. Suitable for support and maintenance tasks.
- Lean:
- Overview: Lean focuses on maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. It is about optimizing the flow of work and continuously improving processes based on feedback.
- Key Principles: Value Stream Mapping, Just-In-Time Delivery, Eliminate Waste, Empower Teams.
- Best For: Organizations focused on efficiency and waste reduction, often in manufacturing or operations.
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe):
- Overview: SAFe is designed for scaling agile practices across large enterprises. It provides a structured approach to aligning teams, programs, and portfolios with business strategy.
- Key Components: Agile Release Trains (ARTs), Program Increments (PIs), Lean Portfolio Management.
- Best For: Large organizations that need to coordinate multiple agile teams across different projects and initiatives.
- Large Scale Scrum (LeSS):
- Overview: LeSS extends Scrum principles to large-scale projects with multiple teams. It maintains simplicity and uses Scrum principles at scale.
- Key Elements: One Product Backlog, One Product Owner, Multiple Teams working in sync.
- Best For: Organizations with multiple teams working on the same product or system, seeking to scale Scrum effectively.
- Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD):
- Overview: DAD provides a hybrid approach, combining agile, lean, and traditional project management practices. It offers a toolkit for scaling agile practices.
- Key Elements: Process Decision Framework, Continuous Delivery, Governance.
- Best For: Organizations with varying project types that need a flexible and tailored approach to scaling agile.
Selecting the Framework:
- Assess Needs: Evaluate the organization's needs, project complexity, team size, and customer requirements.
- Experiment and Adapt: Start with one framework, such as Scrum or Kanban, and adapt as needed. It’s common to start with a smaller scope and expand.
- Consider Scaling: If scaling is required, consider frameworks like SAFe or LeSS that provide guidelines for managing multiple teams.
- Flexibility: Be open to hybrid approaches, combining elements from different frameworks to suit specific needs.
Adopting Agile Frameworks: Mixing and Matching for Flexibility
When organizations embark on an agile transformation, they often take a blended approach, adopting practices from multiple agile frameworks to fit their unique needs. Agile isn't a one-size-fits-all methodology—many organizations combine elements from frameworks like Scrum, Kanban, and Lean to create a hybrid model that best suits their culture, teams, and business goals. This flexibility allows companies to experiment with different practices, integrating what works and discarding what doesn't, creating a custom agile system tailored to their specific context.
For example, some teams may use Scrum to manage software development sprints while leveraging Kanban for continuous flow in operations or support teams. Others may integrate Lean principles to optimize efficiency while maintaining a focus on iterative product development.
However, there are more structured frameworks that provide a clearer roadmap for scaling agile across larger enterprises. One such framework is the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), which offers a more prescriptive approach. Unlike a mix-and-match model, SAFe lays out a specific structure for how agile teams should operate at scale, with clearly defined roles, ceremonies, and processes. It’s designed to align agile practices across multiple teams and departments while maintaining a strong focus on strategic alignment and governance.
While some organizations prefer the flexibility of customizing their agile practices, SAFe offers a more formalized, step-by-step methodology for scaling agile in complex environments, ensuring consistency and structure across the enterprise.
7.2 Establishing Agile Roles and Responsibilities
Agile transformation requires clear roles and responsibilities to ensure that teams are empowered, collaboration is effective, and accountability is maintained. Understanding and defining these roles is critical for implementing agile practices successfully.
Key Agile Roles:
- Product Owner (PO):
- Responsibilities: Define and prioritize the product backlog, ensure the team understands the product vision and goals, act as the voice of the customer, make decisions on feature prioritization, and accept/reject work results.
- Skills: Strong communication, decision-making, and stakeholder management skills. Understanding of customer needs and business objectives.
- Scrum Master:
- Responsibilities: Facilitate Scrum ceremonies, remove impediments, coach the team in agile practices, ensure adherence to Scrum processes, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
- Skills: Strong facilitation, coaching, and conflict resolution skills. Knowledge of agile principles and Scrum methodology.
- Agile Team Members:
- Responsibilities: Collaborate to deliver high-quality work, participate in agile ceremonies, self-organize, and continuously improve their work processes.
- Skills: Technical expertise, problem-solving, teamwork, and adaptability. Ability to work in a cross-functional team environment.
- Agile Coach:
- Responsibilities: Mentor and coach teams, Scrum Masters, and Product Owners. Help the organization embrace agile practices, remove impediments, and promote a culture of agility.
- Skills: Extensive knowledge of agile methodologies, coaching experience, strong communication, and leadership skills.
- Release Train Engineer (RTE) – For Scaled Agile (SAFe):
- Responsibilities: Facilitate Agile Release Train processes, align teams, manage risks and dependencies, and drive continuous improvement in the release process.
- Skills: Program management, facilitation, risk management, and coordination across multiple teams.
Defining Responsibilities:
- Clearly define each role’s responsibilities and expectations.
- Provide role-specific training and resources to ensure team members are equipped to fulfill their roles effectively.
- Encourage collaboration and open communication among roles to ensure alignment and understanding of objectives.
7.3 Implementing Agile Ceremonies
Agile ceremonies are key practices that structure the agile process and facilitate collaboration, planning, and continuous improvement. Each ceremony serves a specific purpose and helps teams stay aligned and focused on delivering value.
Key Agile Ceremonies:
- Daily Stand-up (Daily Scrum):
- Purpose: A short, time-boxed meeting (15 minutes) where team members share what they worked on yesterday, what they plan to work on today, and any blockers they face.
- Outcome: Improved team communication, quick identification of issues, and alignment on daily goals.
- Sprint Planning:
- Purpose: A meeting held at the beginning of each sprint where the team plans the work for the upcoming sprint. The Product Owner presents prioritized items from the backlog, and the team commits to the work they can complete.
- Outcome: A clear sprint goal, a committed sprint backlog, and a shared understanding of what will be delivered.
- Sprint Review:
- Purpose: A meeting held at the end of each sprint to review the completed work with stakeholders. The team demonstrates the product increment, and feedback is collected.
- Outcome: Validation of completed work, stakeholder feedback, and potential adjustments to the product backlog.
- Sprint Retrospective:
- Purpose: A meeting held at the end of each sprint to reflect on the sprint process. The team discusses what went well, what didn’t, and how to improve in the next sprint.
- Outcome: Continuous improvement, action items for process enhancement, and a stronger team dynamic.
- Backlog Refinement:
- Purpose: An ongoing process where the Product Owner and team review and refine the product backlog. Items are clarified, prioritized, and estimated.
- Outcome: A well-defined and prioritized product backlog, ready for future sprints.
Guidelines for Effective Ceremonies:
- Time-boxing: Adhere to strict time limits to keep meetings focused and efficient.
- Participation: Ensure that all team members are involved and actively participate.
- Facilitation: Use skilled facilitators, such as the Scrum Master, to guide discussions and keep meetings on track.
- Feedback: Encourage open and honest feedback to identify areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed.
7.4 Utilizing Agile Tools and Technology
The right tools and technology can significantly enhance the implementation of agile practices by enabling collaboration, visibility, and efficient management of workflows. Selecting and integrating these tools effectively is crucial for supporting agile teams.
Implementing Agile Practices with Kiplot
As organizations transition to agile, having the right tools is crucial for managing workflows, facilitating collaboration, and gaining visibility into portfolio management. Kiplot is an agile portfolio management software that enables organizations to streamline their agile practices while seamlessly integrating with existing tools including Jira, Azure DevOps, SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Office.
Kiplot is designed to support enterprise organizations at every stage of their agile transformation, offering a modular approach that allows businesses to build and customize the platform to suit their unique needs. Whether it’s managing backlogs, aligning teams with strategic goals, or providing real-time visibility into portfolio performance, Kiplot’s suite of capabilities ensure that every aspect of agile workflow is optimized.
Key Features of Kiplot:
- Seamless Integrations: Kiplot integrates with widely-used tools such as Jira for task management, Azure DevOps for development pipelines, SAP and Oracle for enterprise resource planning, and Microsoft Office for collaboration and reporting. This ensures that teams can continue using familiar tools while benefiting from the enhanced visibility and control that Kiplot provides.
- Modular Flexibility: Kiplot offers a modular approach, allowing organizations to add and configure features based on their evolving needs. Whether you're focused on lean portfolio management, resource capacity planning, or agile reporting, Kiplot’s modules can be tailored to support different aspects of your agile framework.
- Real-Time Portfolio Insights: With built-in dashboards and customizable reporting, Kiplot provides real-time insights into portfolio performance, helping teams track progress, manage dependencies, and stay aligned with strategic objectives. This enables decision-makers to make data-driven decisions and keep projects on track.
- Enterprise Scalability: As your organization grows and scales its agile practices, Kiplot can expand alongside it, supporting multiple teams, departments, and geographies. Its enterprise-level capabilities ensure that agile principles are maintained while managing complex portfolios at scale.
By leveraging Kiplot’s powerful suite of features, organizations can streamline their agile transformation efforts, ensuring better collaboration, visibility, and alignment across teams—while integrating seamlessly with the tools they already use.
7.5 Best Practices for Implementing Agile Practices and Tools
- Start Small and Scale: Begin with a few teams or projects to pilot agile practices and tools. Learn from these experiences before scaling to more teams.
- Promote Collaboration: Use tools and practices that enhance collaboration within and across teams. Foster a culture of open communication and teamwork.
- Prioritize Training and Coaching: Invest in training and coaching to build agile capabilities. Continuous learning is key to successful agile transformation.
- Regularly Review and Adapt: Use retrospectives and feedback loops to assess the effectiveness of agile practices and tools. Be willing to make adjustments based on feedback and evolving needs.
- Align with Business Objectives: Ensure that agile practices and tools support the organization’s strategic goals and deliver value to customers.
7.6 Overcoming Challenges in Implementation
Implementing agile practices and tools may come with challenges that need to be addressed proactively to ensure success.
Common Challenges and Solutions:
- Resistance to Change: Address resistance by communicating the benefits of agile practices, involving employees in the transformation process, and providing support to ease the transition.
- Lack of Understanding: Provide comprehensive training and ongoing coaching to ensure teams understand agile principles and how to apply them effectively.
- Tool Overload: Avoid overwhelming teams with too many tools. Select a few core tools that meet the needs and integrate well with each other.
- Siloed Practices: Promote collaboration across teams and departments to break down silos. Use tools and ceremonies that facilitate communication and alignment.
- Maintaining Momentum: Keep the transformation momentum going by celebrating successes, recognizing achievements, and continuously promoting the agile vision.
By carefully selecting agile frameworks, defining roles, implementing ceremonies, and utilizing the right tools, organizations can successfully implement agile practices that enhance collaboration, improve efficiency, and deliver value. This structured approach to implementation ensures that agile principles are integrated into the organization’s ways of working, driving sustainable and impactful transformation.
Section 8: Agile Portfolio Management
8.1 The Importance of Agile Portfolio Management
Agile Portfolio Management is a strategic approach that enables organizations to align projects and initiatives with business objectives while remaining responsive to change. It focuses on delivering maximum value by prioritizing work that aligns with the organization’s goals, managing resources efficiently, and ensuring that teams are working on the right things at the right time.
image:medium
Key Objectives of Agile Portfolio Management:
- Align with Strategic Goals: Ensure that all projects and initiatives are aligned with the organization's strategic objectives, delivering value that supports business priorities.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Efficiently allocate resources based on project priority and organizational capacity, avoiding overloading teams and ensuring optimal use of skills.
- Enhance Visibility and Transparency: Provide real-time visibility into project status, resource utilization, and value delivery, enabling better decision-making and accountability.
- Adapt to Change: Allow the organization to quickly pivot and adjust priorities in response to market changes, customer needs, and emerging opportunities.
8.2 Aligning Projects with Strategic Objectives
For agile portfolio management to be effective, there must be a strong alignment between the organization’s strategic objectives and the projects within its portfolio. This alignment ensures that the work being done is directly contributing to the company’s success and strategic vision.
Steps to Align Projects with Strategic Objectives:
- Define Clear Strategic Goals: Start by defining clear, specific, and measurable strategic objectives. These objectives should reflect the organization's long-term vision and short-term priorities.
- Develop Portfolio Themes: Organize projects into themes or categories that align with strategic goals. Themes could include innovation, customer experience, market expansion, operational efficiency, or digital transformation.
- Use Agile Roadmaps: Create agile roadmaps that map out the high-level vision, goals, and timelines for projects within each theme. Agile roadmaps are flexible and can be adjusted as priorities change.
- Prioritize Projects Based on Value: Use value-based prioritization to decide which projects to undertake. Evaluate potential projects based on their ability to deliver business value, strategic alignment, cost, and risk.
- Regularly Review Alignment: Conduct regular portfolio reviews to ensure ongoing alignment with strategic objectives. Adjust project priorities and resource allocation based on changes in strategy, market conditions, and feedback.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage with key stakeholders, including executives, product owners, and customers, to validate alignment and gather input on strategic priorities.
Tools for Alignment:
- Strategic Planning Workshops: Facilitate workshops to collaboratively define strategic goals and priorities.
- Value Mapping: Use value mapping to visualize the alignment of projects with strategic objectives and assess their potential impact.
- Agile Roadmapping Tools: Utilize agile tools that support dynamic roadmapping, allowing teams to update and adapt plans as needed.
8.3 Prioritizing and Managing the Portfolio Backlog
An essential component of agile portfolio management is the effective prioritization and management of the portfolio backlog. The portfolio backlog is a dynamic list of all the work that could potentially be done, including new projects, features, and improvements. Effective backlog management ensures that the highest-value work is prioritized and that resources are allocated efficiently.
image:medium
Steps for Prioritizing the Portfolio Backlog:
- Establish a Prioritization Framework: Develop a framework for prioritization that considers factors such as business value, customer impact, strategic alignment, cost, and risk. Common prioritization techniques include Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF), MoSCoW (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won't have), and the Eisenhower Matrix.
- Conduct Regular Backlog Refinement: Schedule regular portfolio backlog refinement sessions to review and prioritize items. In these sessions, stakeholders review the backlog, discuss priorities, and make decisions about what to pursue.
- Use a Portfolio Kanban: Implement a portfolio Kanban board to visualize the flow of work from idea to completion. The Kanban board provides visibility into the status of all items in the backlog and helps manage work in progress.
- Limit Work in Progress (WIP): Set WIP limits to avoid overloading teams and ensure that work is completed before new work is started. WIP limits help maintain focus and productivity.
- Adapt Priorities Based on Feedback: Use customer feedback, market insights, and performance data to continuously reassess priorities. Be willing to adjust the backlog as new information emerges or strategic priorities shift.
Managing the Portfolio Backlog:
- Product Owner Involvement: Involve product owners in backlog management to ensure that customer needs and business objectives are represented.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Collaborate with stakeholders across the organization to gather input, discuss priorities, and make informed decisions.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops to gather input from teams, customers, and stakeholders. Use this feedback to refine the backlog and prioritize effectively.
8.4 Resource Allocation and Capacity Planning
Effective resource allocation and capacity planning is critical for agile portfolio management. These practices ensure that the right resources are available for the right projects at the right time, avoiding bottlenecks, reducing waste, and optimizing productivity.
Steps for Resource Allocation and Capacity Planning:
- Assess Resource Availability: Start by assessing the current availability of resources, including team members, skills, tools, and budget. Understand the constraints and capacity of each team.
- Forecast Demand: Forecast future demand based on the prioritized portfolio backlog and upcoming projects. Identify potential resource gaps and plan for additional capacity as needed.
- Allocate Resources Based on Priority: Allocate resources to projects based on their priority and strategic importance. Ensure that high-priority projects have the necessary resources to succeed.
- Balance Capacity and Demand: Use capacity planning techniques to balance the demand for resources with available capacity. Avoid overloading teams and ensure that work is distributed evenly.
- Adjust Allocation as Needed: Continuously monitor resource utilization and adjust allocation as needed. Be flexible and responsive to changes in project priorities, resource availability, and business needs.
Techniques for Effective Resource Allocation:
- Agile Resource Planning Tools: Use agile resource planning tools that provide visibility into resource allocation, utilization, and availability. These tools help teams manage capacity and adjust resources as needed.
- Timeboxing: Use timeboxing to allocate specific time periods for projects or tasks. Timeboxing helps manage capacity and ensures that work is completed within set timeframes.
- Cross-Training: Encourage cross-training to build flexible teams that can adapt to changing resource needs. Cross-trained teams can shift resources more easily based on project priorities.
8.5 Governance in Agile Portfolio Management
Agile portfolio management requires a governance approach that is adaptive, transparent, and aligned with agile principles. Agile governance focuses on enabling teams, providing strategic direction, and ensuring accountability without imposing rigid controls.
image:medium
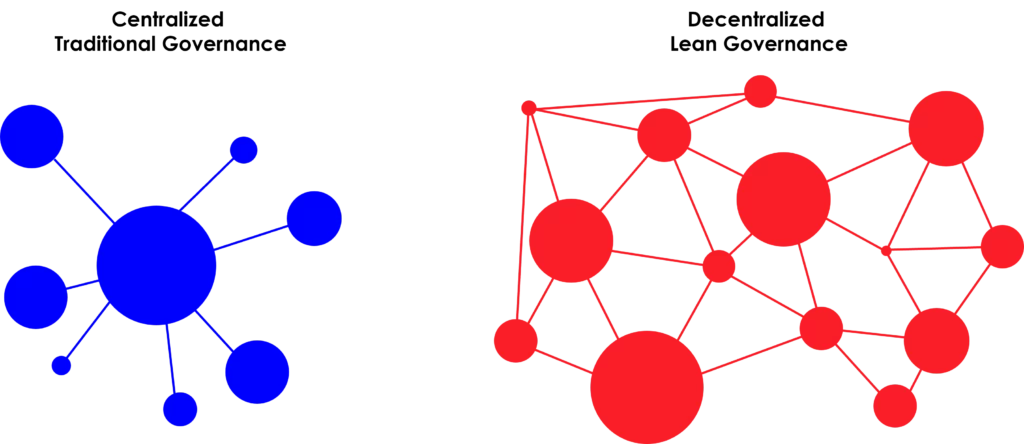
Key Elements of Agile Governance:
- Empower Decision-Making: Empower teams to make decisions about how to achieve their objectives. Decentralized decision-making increases responsiveness and reduces bottlenecks.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensure that portfolio decisions are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals. Use regular portfolio reviews to assess alignment and make adjustments as needed.
- Transparency: Promote transparency in decision-making, project status, and resource allocation. Use dashboards, reports, and visual tools to provide visibility into the portfolio.
- Continuous Improvement: Embed continuous improvement into governance practices. Regularly review governance processes, gather feedback, and make improvements.
- Risk Management: Implement agile risk management practices that focus on early identification, mitigation, and response. Use risk-adjusted backlogs to prioritize work based on risk.
Implementing Agile Governance:
- Portfolio Review Meetings: Conduct regular portfolio review meetings with key stakeholders to discuss progress, challenges, and alignment with strategic objectives. Use these meetings to make informed decisions and adjust the portfolio as needed.
- Agile Steering Committees: Form agile steering committees that include representatives from key functions such as business, IT, and product management. The committee provides strategic oversight, aligns priorities, and supports decision-making.
- Metrics and Dashboards: Use agile metrics and dashboards to provide real-time insights into portfolio performance. Metrics may include time-to-market, customer satisfaction, and value delivered.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms to gather input from teams, stakeholders, and customers. Use this feedback to improve governance practices and enhance portfolio management.
8.6 Measuring Success in Agile Portfolio Management
Measuring success is a critical component of agile portfolio management. It provides insights into how well the portfolio is performing, whether it is delivering value, and where improvements can be made.
Key Metrics for Measuring Success:
- Value Delivery: Measure the value delivered by projects in the portfolio. This may include customer satisfaction, revenue impact, market share, and other key business outcomes.
- Time-to-Market: Track the time it takes for projects to move from concept to delivery. Shorter time-to-market indicates increased efficiency and responsiveness.
- Portfolio Throughput: Measure the number of projects or features delivered within a specific timeframe. Throughput provides insights into productivity and capacity.
- Customer Feedback: Use customer feedback to assess the quality and impact of the work delivered. Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer satisfaction surveys are common tools.
- Alignment with Strategic Goals: Evaluate how well the portfolio aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives. Use strategic alignment matrices to assess this alignment.
Using Metrics for Continuous Improvement:
- Regularly Review Metrics: Review metrics regularly to assess performance and identify areas for improvement. Use metrics to inform decision-making and adjust portfolio management practices.
- Share Insights: Share insights from metrics with teams and stakeholders. Transparency builds trust and encourages collective ownership of success.
- Set Improvement Goals: Use metrics to set specific improvement goals. Focus on enhancing value delivery, reducing time-to-market, and increasing customer satisfaction.
By effectively implementing agile portfolio management, organizations can align their project portfolios with strategic goals, optimize resource allocation, and deliver maximum value. Agile portfolio management enables organizations to stay responsive, adapt to change, and continuously improve, driving sustained success in a dynamic business environment.
Section 9: Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
9.1 Importance of Measuring Success in Agile Transformation
Measuring success is a critical aspect of agile transformation. It provides insight into how effectively agile practices are being adopted, the impact on business outcomes, and areas where improvements can be made. Without measurement, it is difficult to determine whether the transformation is delivering the intended benefits and to make data-driven decisions for ongoing improvement.
Key Objectives of Measuring Success:
- Track Progress: Monitor the progress of agile transformation initiatives against defined goals and objectives.
- Evaluate Impact: Assess the impact of agile practices on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as time-to-market, customer satisfaction, team productivity, and innovation.
- Identify Improvement Areas: Highlight areas where agile practices are succeeding and areas that need enhancement or adjustment.
- Inform Decision-Making: Provide data-driven insights to inform strategic decisions and prioritize efforts in the transformation journey.
- Promote Accountability: Ensure accountability by setting measurable targets and holding teams responsible for achieving them.
9.2 Key Metrics for Measuring Agile Success
Choosing the right metrics is essential for accurately measuring the success of agile transformation. Metrics should be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives, provide meaningful insights, and be actionable.
image:medium
Common Agile Success Metrics:
- Time-to-Market:
- Definition: The time it takes to move a product or feature from concept to customer delivery.
- Importance: Shorter time-to-market indicates increased efficiency and responsiveness to market demands. It demonstrates the ability to deliver value quickly.
- Customer Satisfaction:
- Definition: A measure of how satisfied customers are with the products or services delivered.
- Tools: Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction Surveys, Customer Feedback.
- Importance: High customer satisfaction indicates that agile practices are effectively meeting customer needs and delivering value.
- Team Velocity:
- Definition: The amount of work a team can complete in a sprint, usually measured in story points or completed tasks.
- Importance: Velocity provides insight into team productivity and can help with sprint planning and forecasting.
- Lead Time and Cycle Time:
- Lead Time: The total time from when a request is made to when it is delivered.
- Cycle Time: The time it takes to complete a specific task or work item from start to finish.
- Importance: Shorter lead and cycle times indicate efficient processes and the ability to deliver quickly.
- Quality Metrics:
- Definition: Measures of product or service quality, such as defect rates, bug counts, or code quality.
- Importance: High-quality deliverables are critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and reducing the cost of rework.
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction:
- Definition: Measures of how engaged and satisfied employees are with their work environment, including surveys and feedback.
- Importance: Engaged employees are more productive, innovative, and committed to continuous improvement.
- Innovation Rate:
- Definition: The frequency and impact of new ideas or features introduced to the market.
- Importance: A high innovation rate indicates that the organization is effectively leveraging agile practices to drive innovation.
- Alignment with Strategic Goals:
- Definition: A measure of how well projects and initiatives align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Importance: Ensuring alignment with strategic goals is critical for delivering value that supports the organization’s long-term vision.
9.3 Establishing a Measurement Framework
To effectively measure success, it is important to establish a structured measurement framework. This framework should define the metrics to be tracked, how they will be measured, and how the data will be used to drive continuous improvement.
Steps to Establish a Measurement Framework:
- Define Metrics: Identify the key metrics that align with the organization’s strategic objectives and agile transformation goals. Metrics should be specific, measurable, and relevant.
- Set Baselines and Targets: Establish baseline measurements to understand the current state. Set specific targets for each metric to define what success looks like.
- Collect Data: Determine how data will be collected for each metric. Use tools, surveys, feedback loops, and automated systems to gather data consistently and accurately.
- Analyze and Report: Regularly analyze the data to track progress against targets. Use dashboards and reports to provide visibility into key metrics and share insights with stakeholders.
- Review and Adjust: Conduct regular reviews of the measurement framework to ensure it remains aligned with the organization’s goals. Be willing to adjust metrics, targets, and data collection methods based on feedback and changing priorities.
Tools for Measurement:
- Agile Project Management Tools: Tools like Kiplot provide built-in metrics and reporting features to track team velocity, cycle time, and other agile metrics.
- Feedback Systems: Use customer feedback tools (e.g., NPS surveys) and employee engagement surveys to gather insights into satisfaction and engagement.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Use data analytics platforms to aggregate and analyze data from multiple sources, providing a holistic view of agile performance.
9.4 Continuous Improvement through Retrospectives
Retrospectives are a core practice in agile methodology that enable teams to reflect on their work, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments. Regular retrospectives are essential for fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Conducting Effective Retrospectives:
- Schedule Regular Retrospectives: Hold retrospectives at the end of each sprint or iteration. This regular cadence ensures that teams have frequent opportunities to reflect and improve.
- Create a Safe Environment: Foster an environment where team members feel safe to share their thoughts, ideas, and concerns. Psychological safety is key to open and honest communication.
- Use Structured Techniques: Use structured techniques, such as the “Start, Stop, Continue” method or the “Five Whys,” to facilitate discussions and identify improvement areas.
- Focus on Actionable Outcomes: Ensure that retrospectives result in specific, actionable items that the team commits to implementing in the next iteration. Assign ownership to these actions to ensure accountability.
- Follow Up: Review the outcomes of previous retrospectives to track progress and ensure that improvement actions are being implemented. Adjust as necessary based on feedback and results.
Example Retrospective Questions:
- What went well during this sprint?
- What didn’t go as planned, and why?
- What can we do differently to improve in the next sprint?
- Are there any blockers or impediments that need to be addressed?
9.5 Implementing a Culture of Continuous Improvement
A culture of continuous improvement goes beyond individual retrospectives and becomes ingrained in the organization’s way of working. It requires commitment from leadership, a mindset of learning, and mechanisms for capturing and acting on feedback.
Strategies for Fostering Continuous Improvement:
- Lead by Example: Leadership should model continuous improvement behaviors. Leaders should regularly seek feedback, acknowledge mistakes, and demonstrate a commitment to learning.
- Empower Teams: Empower teams to take ownership of their improvement efforts. Provide the autonomy and resources they need to experiment, innovate, and implement changes.
- Encourage Experimentation: Create a safe environment where experimentation is encouraged. Allow teams to try new approaches, learn from failures, and iterate on their processes.
- Provide Training and Development: Invest in training and development programs that enhance skills and knowledge. Encourage continuous learning through workshops, courses, and certifications.
- Recognize Improvement Efforts: Recognize and celebrate teams and individuals who contribute to continuous improvement. Highlight success stories and share examples of positive change.
- Implement Feedback Mechanisms: Establish regular feedback mechanisms to gather insights from employees, customers, and stakeholders. Use surveys, feedback sessions, and suggestion boxes to collect input.
9.6 Leveraging Agile Metrics for Strategic Decision-Making
Agile metrics are not only useful for tracking progress and improvement but also play a critical role in strategic decision-making. By analyzing metrics, organizations can make informed decisions that drive business success and agility.
Using Metrics for Strategic Decision-Making:
- Identify Trends and Patterns: Analyze metrics over time to identify trends and patterns. Understanding these trends can provide insights into productivity, efficiency, and areas for improvement.
- Align with Strategic Goals: Use metrics to assess how well the organization is achieving its strategic goals. Ensure that the metrics tracked are directly related to the organization’s objectives.
- Prioritize Initiatives: Use data to prioritize initiatives based on their impact on key metrics. Focus resources and efforts on projects that deliver the highest value and align with strategic priorities.
- Adapt to Changing Conditions: Use metrics to identify changes in customer needs, market conditions, or internal capabilities. Be prepared to pivot and adjust strategies based on these insights.
- Communicate Insights: Share insights from metrics with stakeholders across the organization. Use visual dashboards and reports to communicate progress, highlight successes, and identify areas for improvement.
By measuring success and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can ensure that their agile transformation delivers lasting value. Agile metrics provide the data-driven insights needed to track progress, make informed decisions, and drive continuous improvement, enabling organizations to remain competitive, responsive, and successful in a rapidly changing environment.
Section 10: Sustaining the Transformation
10.1 Importance of Sustaining Agile Transformation
Successfully implementing agile practices is only the beginning of an organization’s agile journey. To realize the full benefits of agility, it’s crucial to sustain the transformation over the long term. Sustaining agile transformation involves embedding agile principles into the organizational culture, continuously supporting teams, and ensuring that agile practices evolve to meet changing needs. Without sustained commitment, there is a risk of reverting to old habits and ways of working (such as Waterfall) and losing the progress made.
Key Objectives of Sustaining Agile Transformation:
- Embed Agile Culture: Ensure that agile principles become part of the organization’s DNA, influencing decision-making, behaviors, and practices across all levels.
- Continuous Support and Coaching: Provide ongoing support, training, and coaching to teams to reinforce agile practices and address challenges.
- Adapt and Evolve: Keep agile practices relevant by adapting to new challenges, technologies, and market conditions. Embrace continuous improvement and innovation.
- Maintain Leadership Commitment: Ensure ongoing commitment from leadership to support agile initiatives and provide the necessary resources and guidance.
10.2 Establishing an Agile Center of Excellence (CoE)
An Agile Center of Excellence (CoE) is a dedicated team or function that provides ongoing support, governance, and leadership for agile practices across the organization. The CoE acts as a central hub for agile knowledge, resources, and best practices, helping to sustain and scale agile transformation.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Agile CoE:
- Training and Development: Develop and deliver training programs to build agile competencies across the organization. Provide workshops, certifications, and learning resources to enhance skills.
- Coaching and Mentoring: Offer coaching and mentoring support to agile teams, Scrum Masters, Product Owners, and other roles. Coaches help teams overcome challenges, improve processes, and adopt best practices.
- Standardization of Practices: Define and standardize agile practices, tools, and methodologies to ensure consistency and alignment across teams. Develop templates, guidelines, and playbooks for agile processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Drive continuous improvement initiatives by collecting feedback, identifying areas for enhancement, and implementing changes. Use retrospectives and other feedback mechanisms to gather insights.
- Measurement and Reporting: Develop metrics and dashboards to track the success of agile practices. Provide visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) and use data to inform decision-making.
- Knowledge Sharing: Facilitate knowledge sharing and collaboration across teams. Organize communities of practice, forums, and knowledge-sharing sessions to promote learning and innovation.
- Change Management: Support change management efforts by communicating the benefits of agile, addressing resistance, and helping teams navigate the transformation journey.
Setting Up an Agile CoE:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and scope of the Agile CoE. Align the CoE’s goals with the organization’s strategic objectives and agile transformation goals.
- Select CoE Members: Assemble a team of experienced agile practitioners, coaches, and leaders who can provide guidance and support. Include representatives from key functions, such as IT, product management, and HR.
- Develop a Roadmap: Create a roadmap for the Agile CoE, outlining its activities, initiatives, and milestones. The roadmap should include training programs, coaching plans, and continuous improvement initiatives.
- Secure Leadership Support: Obtain support from leadership to provide the necessary resources and authority for the CoE. Leadership endorsement is critical for the CoE’s success.
- Communicate the CoE’s Role: Clearly communicate the role, objectives, and services of the Agile CoE to the organization. Ensure that teams understand how to access support and resources from the CoE.
image:medium
10.3 Leadership’s Role in Sustaining Agile Transformation
Leadership plays a vital role in sustaining agile transformation. Leaders set the tone for the organization, influence culture, and provide the direction and support needed to embed agile practices.
Leadership Responsibilities for Sustaining Agile Transformation:
- Champion Agile Principles: Leaders should actively champion agile principles and values. They should model agile behaviors, such as collaboration, transparency, and a focus on customer value.
- Provide Vision and Direction: Leaders should provide a clear vision for the organization’s agile journey. They should articulate how agile supports the organization’s strategic goals and inspire teams to embrace agility.
- Support Teams: Leaders should provide the necessary resources, tools, and training to support agile teams. They should remove obstacles, enable decision-making, and empower teams to succeed.
- Engage in Continuous Improvement: Leaders should participate in continuous improvement efforts. They should regularly seek feedback, review performance metrics, and make adjustments to support agile practices.
- Communicate Consistently: Leaders should communicate consistently about the progress of agile transformation. Regular updates build trust, keep employees informed, and reinforce commitment to agile principles.
- Recognize and Reward Success: Leaders should recognize and celebrate the achievements of agile teams. Acknowledging successes reinforces positive behaviors and motivates teams to continue their efforts.
Developing Agile Leadership:
- Leadership Training: Provide agile leadership training to develop the skills and mindset needed to lead in an agile environment. Focus on servant leadership, coaching, and facilitation.
- Agile Leadership Community: Create a community of agile leaders who can share experiences, challenges, and best practices. Encourage collaboration and learning among leaders.
- Mentoring Programs: Implement mentoring programs where experienced agile leaders mentor new leaders. Mentoring provides guidance, support, and knowledge transfer.
10.4 Embedding Agile into Organizational Culture
To sustain agile transformation, agile principles must be embedded into the organizational culture. This requires a shift in mindset, values, and behaviors that align with agility.
Steps to Embed Agile into Culture:
- Define Agile Values: Clearly define the core values that underpin agile practices, such as collaboration, transparency, customer focus, and continuous improvement. Communicate these values consistently.
- Align Policies and Processes: Ensure that organizational policies, processes, and structures support agile principles. Review and adapt policies related to decision-making, performance evaluation, and resource allocation.
- Promote Agile Behaviors: Encourage behaviors that align with agile values. Recognize and reward collaboration, innovation, and adaptability. Provide feedback to reinforce positive behaviors.
- Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration: Break down silos and promote collaboration across teams and departments. Use cross-functional teams, shared goals, and joint initiatives to foster collaboration.
- Build a Learning Culture: Foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encourage employees to seek out learning opportunities, share knowledge, and experiment with new ideas.
- Use Agile Ceremonies: Incorporate agile ceremonies, such as daily stand-ups, retrospectives, and planning sessions, into the organization’s routines. These ceremonies reinforce agile principles and encourage reflection and improvement.
10.5 Maintaining Momentum and Adaptability
Sustaining agile transformation requires maintaining momentum and being adaptable to change. Organizations must continue to innovate, adapt, and respond to new challenges and opportunities.
Strategies for Maintaining Momentum:
- Celebrate Successes: Regularly celebrate successes and achievements. Recognize milestones, project completions, and examples of exceptional teamwork. Celebrations boost morale and motivation.
- Keep the Vision Alive: Continuously communicate the agile vision and how it aligns with the organization’s goals. Remind teams of the purpose and benefits of agile transformation.
- Encourage Innovation: Create an environment where innovation is encouraged and supported. Allow teams to experiment with new ideas, technologies, and practices. Provide time and resources for innovation.
- Adapt to Change: Be open to adapting agile practices based on feedback, new insights, and changing business needs. Use retrospectives and feedback loops to gather input and make adjustments.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor the progress of agile transformation. Use metrics, surveys, and feedback to assess how well agile practices are being sustained. Review and refine strategies to address challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
10.6 Scaling Agile Across the Organization
As agile practices become embedded, the next step is to scale agile across the organization. Scaling involves extending agile practices to more teams, departments, and functions, ensuring that agility is consistent and widespread.
Steps to Scale Agile:
- Use Scaling Frameworks: Consider using scaling frameworks such as SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework), LeSS (Large Scale Scrum), or Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD) to provide structure and guidance for scaling agile practices.
- Develop a Scaling Plan: Create a scaling plan that outlines how agile practices will be extended to new teams and areas. Define the steps, timelines, and resources needed for scaling.
- Provide Scaling Support: Offer training, coaching, and resources to support teams as they adopt agile practices. Use the Agile CoE to provide guidance and support.
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure consistency in agile practices across teams. Develop standard templates, guidelines, and processes that align with agile principles.
- Foster a Scalable Culture: Promote a culture that supports scalability. Encourage collaboration across teams, shared goals, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
- Monitor Scaling Efforts: Track the progress of scaling efforts using metrics and feedback. Make adjustments as needed to ensure successful scaling and sustained agility.
By focusing on sustaining agile transformation, organizations can ensure that agile practices become deeply rooted in their culture, driving long-term success and adaptability. Sustaining transformation requires commitment from leadership, continuous support, and a willingness to evolve and innovate. With the right strategies in place, organizations can maintain momentum, scale agile practices, and thrive in a dynamic and competitive environment.
Section 11: Conclusion and Next Steps
11.1 Key Takeaways
The journey to agile transformation is an ongoing process that requires commitment, collaboration, and a willingness to adapt. This playbook has outlined a comprehensive approach to achieving and sustaining agile transformation, covering essential aspects such as understanding agile principles, aligning projects with strategic goals, building agile teams, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Here are the key takeaways.
- Start with a Clear Vision and Strategy: Defining a clear vision for agile transformation and aligning it with the organization's strategic objectives is crucial. This vision should be communicated effectively to inspire and guide the entire organization.
- Assess and Understand the Current State: Before embarking on transformation, assess the organization's current state, identify strengths and weaknesses, and understand cultural and operational readiness for agile practices.
- Design a Phased Transformation Roadmap: A structured, phased approach to agile transformation helps manage complexity, reduce risks, and build momentum. Starting with pilot projects, scaling agile practices, and achieving enterprise-wide adoption are critical steps in the journey.
- Build Agile Teams and Culture: Agile teams are the foundation of successful transformation. Fostering a culture of collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement is essential for sustaining agility.
- Implement Agile Practices and Tools: Selecting the right agile frameworks, defining roles, conducting agile ceremonies, and utilizing effective tools are key components of implementing agile practices successfully.
- Engage in Agile Portfolio Management: Aligning projects with strategic goals, prioritizing work based on value, and managing resources effectively are central to agile portfolio management. Continuous monitoring and adjustment ensure that the portfolio delivers maximum value.
- Measure Success and Drive Continuous Improvement: Establishing a measurement framework, tracking key metrics, conducting retrospectives, and embracing a culture of continuous improvement are vital for sustaining agile transformation.
- Sustain the Transformation: Embedding agile principles into the organizational culture, establishing an Agile Center of Excellence, maintaining leadership commitment, and scaling agile practices are crucial for sustaining long-term agility.
11.2 The Road Ahead: Embarking on Your Agile Transformation
Agile transformation is not a one-time project but an ongoing journey of evolution and adaptation. As you move forward, it's essential to remain committed to the principles and practices that drive agility. Here are the next steps to take as you embark on or continue your agile journey:
- Commit to Continuous Learning: Agile transformation is a learning journey. Encourage teams to continuously seek new knowledge, experiment with innovative practices, and learn from their experiences. Invest in training, workshops, and certifications to build agile skills.
- Foster a Culture of Experimentation: Create an environment where experimentation is encouraged, and failures are seen as opportunities for learning. Empower teams to test new ideas, iterate, and improve continuously.
- Engage with the Agile Community: Connect with the broader agile community to share insights, learn from others, and stay informed about emerging trends and best practices. Participate in agile conferences, meetups, and online forums to build connections and exchange knowledge.
- Adapt to Changing Needs: Stay adaptable and responsive to changes in the market, customer needs, and technological advancements. Be willing to pivot and adjust agile practices to meet new challenges and opportunities.
- Measure and Celebrate Success: Regularly measure progress and celebrate successes. Recognize the achievements of teams and individuals who contribute to the agile journey. Celebrating successes reinforces positive behaviors and motivates teams.
- Continuously Evolve the Agile Roadmap: The agile roadmap should be a living document that evolves based on feedback, insights, and changing priorities. Regularly review and update the roadmap to ensure it remains relevant and aligned with strategic goals.
- Engage Leadership and Stakeholders: Keep leadership and stakeholders engaged and informed about the progress of agile transformation. Their ongoing support is critical for sustaining momentum and ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
11.3 Encouraging a Mindset of Agility
Agile transformation goes beyond adopting new practices and tools; it requires a mindset shift towards agility. An agile mindset emphasizes flexibility, customer focus, collaboration, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Here are some key principles to cultivate an agile mindset:
- Embrace Change: View change as an opportunity rather than a threat. Be open to new ideas, approaches, and ways of working. Agility thrives in environments that welcome change and innovation.
- Focus on Customer Value: Prioritize delivering value to customers. Understand their needs, gather feedback, and continuously refine products and services to meet those needs effectively.
- Collaborate and Communicate: Encourage open communication and collaboration across teams and departments. Break down silos, share knowledge, and work together towards common goals.
- Learn from Failure: See failure as a learning opportunity. Encourage teams to take calculated risks, experiment, and learn from their experiences. Use failures as a chance to improve and innovate.
- Continuously Improve: Commit to continuous improvement at all levels of the organization. Regularly reflect on processes, practices, and outcomes, and seek ways to enhance efficiency, quality, and value delivery.
11.4 Commit to Agile Transformation
Agile transformation is a journey that requires commitment, perseverance, and collaboration. Whether you are just beginning your agile journey or looking to scale and sustain your agile practices, now is the time to commit to agility. By embracing agile principles, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and staying focused on delivering value, your organization can achieve lasting success in a rapidly changing world.
Take Action Today:
- Start with Small Steps: Begin with pilot projects to demonstrate the value of agile practices. Use early successes to build momentum and support for scaling agile transformation.
- Invest in Training and Development: Equip your teams with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed. Offer training, coaching, and resources to support their growth.
- Engage Leadership and Stakeholders: Involve leadership and key stakeholders in the agile journey. Their support is critical for driving change and achieving alignment with strategic objectives.
- Measure Progress and Adjust: Use metrics to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. Be willing to adjust your approach based on feedback and insights.
- Celebrate Milestones: Recognize and celebrate achievements along the way. Celebrating milestones reinforces positive behaviors and motivates teams to continue their efforts.
By committing to agile transformation, your organization can unlock the potential for greater innovation, responsiveness, and customer satisfaction. Embrace the journey, and let agility be the driving force behind your success.
Section 12: Drive Your Agile Transformation with Kiplot
If you’re looking to dive deeper into agile transformation and the key principles that drive successful agile organizations, visit Kiplot's Knowledge Center. Our comprehensive resources cover everything from agile methodologies to real-world case studies, helping you understand how to implement agile practices effectively within your teams.
Ready to take the next step in your agile journey? Explore Kiplot's Agile Portfolio Management Software, specifically designed for enterprise-level agility. Whether you’re scaling agile across your organization or optimizing your portfolio management, Kiplot offers the tools and insights needed to drive value, enhance collaboration, and achieve strategic alignment.