Introduction
In value-driven markets, organizations must adapt and deliver value continuously. Yet organizations are held back by traditional governance and decision-making frameworks that fail to keep pace with the demands for agility and innovation. For companies adopting Lean Portfolio Management (LPM) practices within the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), a radical rethinking of these processes is not just beneficial to delivery—it's imperative.
By adopting LPM principles and integrating them with SAFe, organizations can achieve a more responsive and efficient approach to governance. Not only aligning investments with strategic priorities, but also empowering teams to make decisions with a degree of autonomy.
In this article, we will explore how to optimize governance and decision-making in the context of LPM, enabling organizations to unlock the full potential enterprise agility within SAFe.
For those looking for a high-level introduction to Lean Portfolio Management and SAFe – click here to read our introductory guide.
💡 What is governance in Lean Portfolio Management? Governance in the context of lean portfolio management refers to the structures, processes, and policies that guide and control how an organization’s portfolio of projects and initiatives are managed and executed. Lean governance emphasizes efficiency, flexibility, and alignment with strategic goals, ensuring that resources are optimally allocated, decisions are made quickly and effectively, and projects deliver maximum value to the organization.
The limitations of traditional governance models
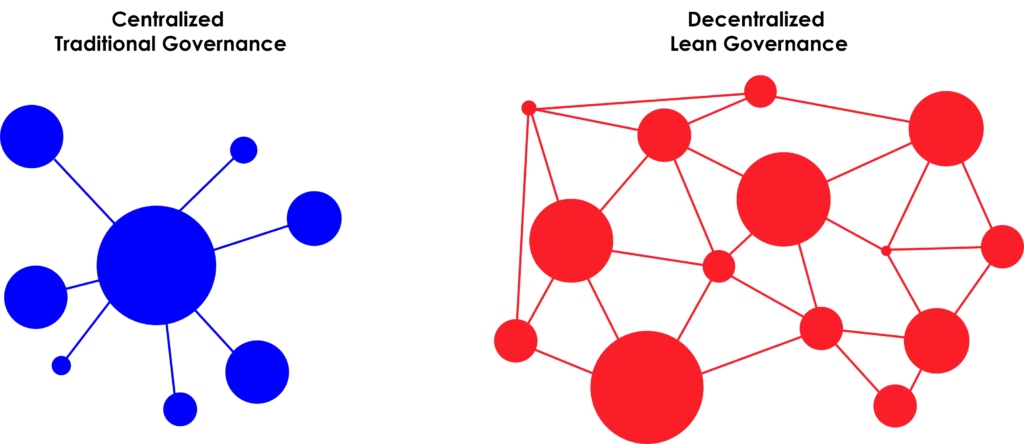
Traditional governance models are fraught with inefficiencies and bureaucratic hurdles that impede decision-making and stifle innovation. Extensive documentation and multi-layered approval processes that stretch high up the org chart mean that delays to key decisions are commonplace, hindering an organization’s ability to respond rapidly to market changes.
The centralized control characteristic of these models also places decision-making authority far from the actual work. The result? Misaligned priorities and decisions that lack the immediacy and context of ground-level insights. The rigidity in traditional governance structures further exacerbates these issues, as predefined procedures fail to accommodate the dynamism and pace required in modern markets, hampering an organization's ability to act quickly and decisively.
Role of governance in SAFe LPM
Lean governance within SAFe focuses on enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and strategic alignment. By reducing overheads and enabling faster decision-making, it ensures that investments align with strategic goals, maximizing value delivery.
One of the key principles of lean governance is decentralizing decision-making authority to the teams directly executing the work. This decentralization accelerates decision-making, fosters a culture of accountability and empowerment, and enhances overall productivity.
Organizing work around value streams instead of functional silos ensures that all activities are concentrated on delivering customer value. This change of approach breaks down traditional barriers and promotes cross-functional collaboration between teams.
Incorporating continuous feedback and learning, this approach supports the continuous flow of value and enables organizations to operate with agility. By prioritizing strategic alignment and operational flexibility, lean governance within SAFe provides a comprehensive framework for managing complex portfolios, making it responsive to both organizational needs and market dynamics.
Effective lean governance practices for success
Below are some key behaviors and practices that benefit organizations adopting a lean governance culture.
Strategic Alignment and Investment Funding:
- Dynamic Funding Models: Replace annual budgeting cycles with dynamic funding models that allow for frequent reallocation of resources based on changing priorities and market conditions. This approach ensures that investments are continuously aligned with strategic goals.
- Strategic Themes and Portfolio Vision: Use strategic themes and a clear portfolio vision to guide investment decisions. Strategic themes provide a high-level direction, while the portfolio vision ensures that all initiatives contribute to the overarching goals.
Lean Budgeting:
- Guardrails: Implement financial and performance guardrails that provide a framework for decision-making without stifling innovation. These guardrails define boundaries within which teams can operate autonomously.
- Participatory Budgeting: Engage key stakeholders in the budgeting process to ensure that investment decisions are well-informed and aligned with both strategic goals and operational realities.
Operational Focus:
- Continuous Planning: Move away from fixed planning cycles to continuous planning and PI (Program Increment) Planning, which allows for ongoing adjustment of priorities and resource allocation based on real-time feedback and performance data.
- Flow Metrics: Utilize flow metrics, such as cycle time and throughput, to measure and manage the efficiency of value delivery. These metrics provide insights into process bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
How to optimize decision making in lean portfolios
Empowering teams, increasing transparency, and leveraging data are critical for enhancing decision-making processes within lean portfolios. By implementing the following practices, organizations can achieve more effective and agile decision-making.
Empowerment and Autonomy:
- Delegation of Authority: Clearly define decision-making authority at all levels, ensuring that decisions are made by those with the most relevant information and expertise. This delegation requires a high degree of trust and a culture that supports empowerment.
- Decision-making Frameworks: Develop and utilize decision-making frameworks that provide guidelines for making informed and consistent decisions. These frameworks should balance autonomy with alignment to strategic objectives.
Transparency and Visibility:
- Visual Management Tools: Implement visual management tools, such as Kanban boards and dashboards, to provide real-time visibility into work progress and performance. These tools help ensure that all stakeholders have access to the information needed for effective decision-making.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews, such as PI (Program Increment) Planning and portfolio sync meetings, to assess progress, discuss challenges, and make necessary adjustments. These reviews foster a culture of continuous improvement and alignment.
Data-Driven Decisions:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish KPIs that are aligned with strategic goals and use these metrics to guide decision-making. KPIs should cover various aspects of performance, including financial, operational, and customer satisfaction.
- Analytics and Insights: Leverage data analytics to gain deeper insights into performance trends and inform strategic decisions. Advanced analytics can help identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize resource allocation.
Overcoming challenges in governance and decision-making
Addressing cultural shifts, balancing control with flexibility, and fostering continuous improvement are key challenges for organizations adopting lean governance. Below are some practical strategies to navigate these challenges.
Cultural Shifts:
- Change Management: Implement a robust change management strategy to support the cultural shift towards lean governance. This includes training, communication, and leadership support to foster a mindset of trust, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
- Leadership Commitment: Secure commitment from leadership to champion the shift towards lean governance and decentralized decision-making. Leaders should model the behaviors and values that support this new approach.
Balancing Control and Flexibility:
- Risk Management: Develop risk management strategies that balance the need for control with the flexibility required for agile decision-making. This includes identifying potential risks, establishing mitigation plans, and continuously monitoring risk factors.
- Adaptive Policies: Create adaptive policies that provide guidance without imposing unnecessary constraints. These policies should be regularly reviewed and updated based on feedback and changing circumstances.
Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Loops: Establish robust feedback loops to gather insights from all levels of the organization. Use this feedback to refine governance and decision-making processes continually.
- Iterative Refinement: Adopt an iterative approach to refining governance practices, using lessons learned from each cycle to make incremental improvements. This approach ensures that governance evolves in response to emerging challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion
Effective governance and decision-making are pivotal components of SAFe LPM. By adopting lean governance practices, organizations can shifting decision-making authority closer to the teams, utilizie dynamic funding models, and embrace continuous planning to drive key initiatives that deliver agility and value.
For more in-depth insights and strategies on governance and decision-making within SAFe LPM, explore the wealth resources available in the our Knowledge Center. Here, you'll find articles and whitepapers to support your agile transformation.
Learn how Kiplot’s Lean Portfolio Management Software can enable your organization to achieve enterprise agility in alignment with SAFe principles. Discover how Kiplot helps bridge the gap between strategy and execution, ensuring your projects are aligned with strategic objectives and delivering measured value.

